Connecting to SSL services
Platform Notice: Data Center Only - This article only applies to Atlassian products on the Data Center platform.
Note that this KB was created for the Data Center version of the product. Data Center KBs for non-Data-Center-specific features may also work for Server versions of the product, however they have not been tested. Support for Server* products ended on February 15th 2024. If you are running a Server product, you can visit the Atlassian Server end of support announcement to review your migration options.
*Except Fisheye and Crucible
Summary
The content on this page relates to platforms which are not supported. Consequently, Atlassian Support cannot guarantee providing any support for it. Please be aware that this material is provided for your information only and using it is done so at your own risk.
Problem
This page describes how to get web applications like Jira and Confluence connecting to external servers over SSL, via the various SSL-wrapped protocols. For instance, you may want to:
Refer to an
https://...URL in a Confluence macroUse an IMAPS server to retrieve mail in Jira
Use SMTP over SSL (SMTPS) to send mail in Jira
Connect to an LDAP directory over SSL
Set up Application Links over SSL
This does not cover running your application over SSL. Please see your product's documentation to run it over SSL:
Application | Using SSL with your application |
|---|---|
JIRA applications | Running JIRA applicatioRunning JIRA applications over SSL or HTTPSns over SSL or HTTPS |
Confluence | |
Bamboo | |
Bitbucket Server (previously called Stash) | Securing Bitbucket Server with SSL (terminating at Tomcat) |
Fisheye / Crucible |
Diagnosis
Attempting to access URLs that are encrypted with SSL (for example HTTPS, LDAPS, IMAPS) throws an exception and your application refuses to connect to it. For example:
1
2
3
4
javax.net.ssl.SSLHandshakeException: sun.security.validator.ValidatorException: PKIX path building failed: sun.security.provider.certpath.SunCertPathBuilderException: unable to find valid certification path to requested target
at com.sun.mail.imap.IMAPStore.protocolConnect(IMAPStore.java:441)
at javax.mail.Service.connect(Service.java:233)
at javax.mail.Service.connect(Service.java:134)This is the same as the following error that's generated in Chrome when visiting a page that's encrypted with a self-signed certificate, except Java can't "Proceed anyway", it just refuses the certificate:
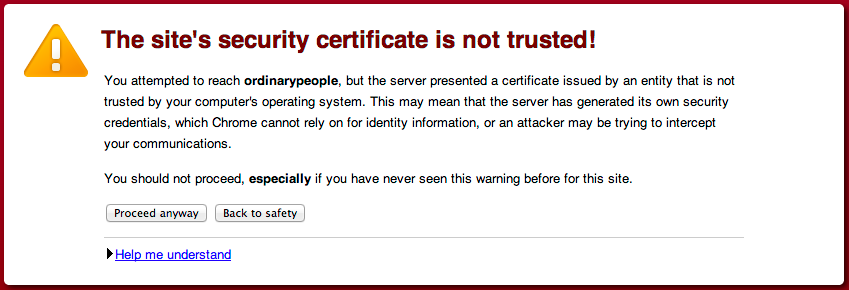
Cause
Whenever your application attempts to connect to another application over SSL (e.g.: HTTPS, IMAPS, LDAPS), it will only be able to connect to that application if it can trust it. The way trust is handled in the Java world (this is what your application is written in) is that you have a "truststore" file (typically $JAVA_HOME/lib/security/cacerts). This trust store file contains trusted certificates and Java uses this to determine if the SSL certificate used by another application can be trusted. Java will only trust certificates that are signed by a Certificate Authority (CA) whose certificate is in the trust store, or public certificates that are added to the trust store. For example, if we look at the certificate for Atlassian:
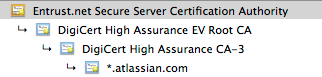
We can see the *.atlassian.com certificate has been signed by the intermediate certificates, DigiCert High Assurance EV Root CA and DigiCert High Assurance CA-3. These intermediate certificates have been signed by the root Entrust.net Secure Server CA. Those three certificates combined are referred to as the certificate chain. Because the three CA certificates are within the Java trust store file (cacerts), Java will trust any certificates signed by them (in this case, *.atlassian.com). Alternatively, if the *.atlassian.com certificate was in the trust store, Java would also trust that site.
This problem comes from a certificate that is either self-signed (a CA did not sign it) or the certificate chain does not exist within the Java trust store. Subsequently, your application doesn't trust the certificate and fails to connect to the application.
Solution
Resolution
In order to resolve this, the public certificate needs to be imported in the Java trust store that your application uses. In the example above, this is *.atlassian.com and we cover how to install it below.
Was this helpful?