Resolving SSL Self-Signed Certificate Errors on Bitbucket Datacenter
Platform notice: Server and Data Center only. This article only applies to Atlassian products on the Server and Data Center platforms.
Support for Server* products ended on February 15th 2024. If you are running a Server product, you can visit the Atlassian Server end of support announcement to review your migration options.
*Except Fisheye and Crucible
Problem
If you're using a self-signed certificate on your Bitbucket Datacenter, you may receive SSL certificate errors when you try to perform certain actions. This page will help you resolve these errors.
When trying to perform a clone using instructions stated in Debug logging for Git operations on the client the following error is reported:
$ export GIT_CURL_VERBOSE=1
$ git clone https://username@git.example.com/scm/repository.git
Cloning into 'repository'...
* Couldn't find host git.example.com in the _netrc file; using defaults
* Adding handle: conn: 0x22a7568
* Adding handle: send: 0
* Adding handle: recv: 0
* Curl_addHandleToPipeline: length: 1
* - Conn 0 (0x22a7568) send_pipe: 1, recv_pipe: 0
* About to connect() to git.example.com port 443 (#0)
* Trying 10.253.136.142...
* Connected to git.example.com (10.253.136.142) port 443 (#0)
* successfully set certificate verify locations:
* CAfile: C:\Program Files (x86)\Git/bin/curl-ca-bundle.crt
CApath: c:/Users/username/Downloads
* SSL certificate problem: self signed certificate in certificate chain
* Closing connection 0
fatal: unable to access 'https://username@git.example.com/scm/repository.git': SSL certificate problem: self signed certificate in certificate chain
Cause
This is caused by Git not trusting the certificate provided by your server.
Workaround
One possible workaround is to temporarily disable SSL check for your git command in case you only need to perform a one-time clone:
GIT_SSL_NO_VERIFY=true git clone https://username@git.example.com/scm/repository.git
or
git remote add origin <gitrepo>
git config --global http.sslVerify falseThe workaround is intended to be used for one-time only operations and not to be used frequently. Removing the SSL verification disproves the whole concept of having SSL implemented.
Resolution
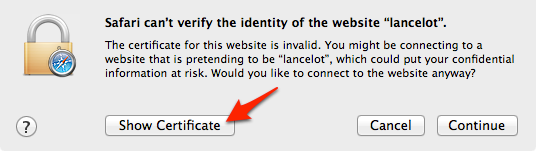
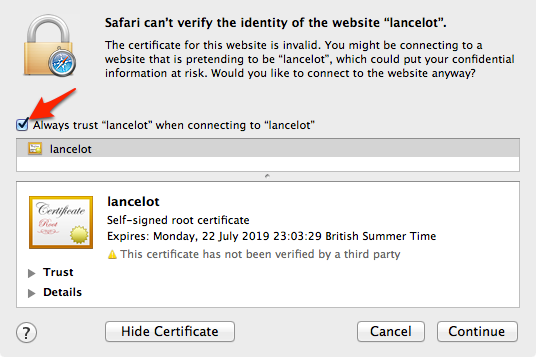
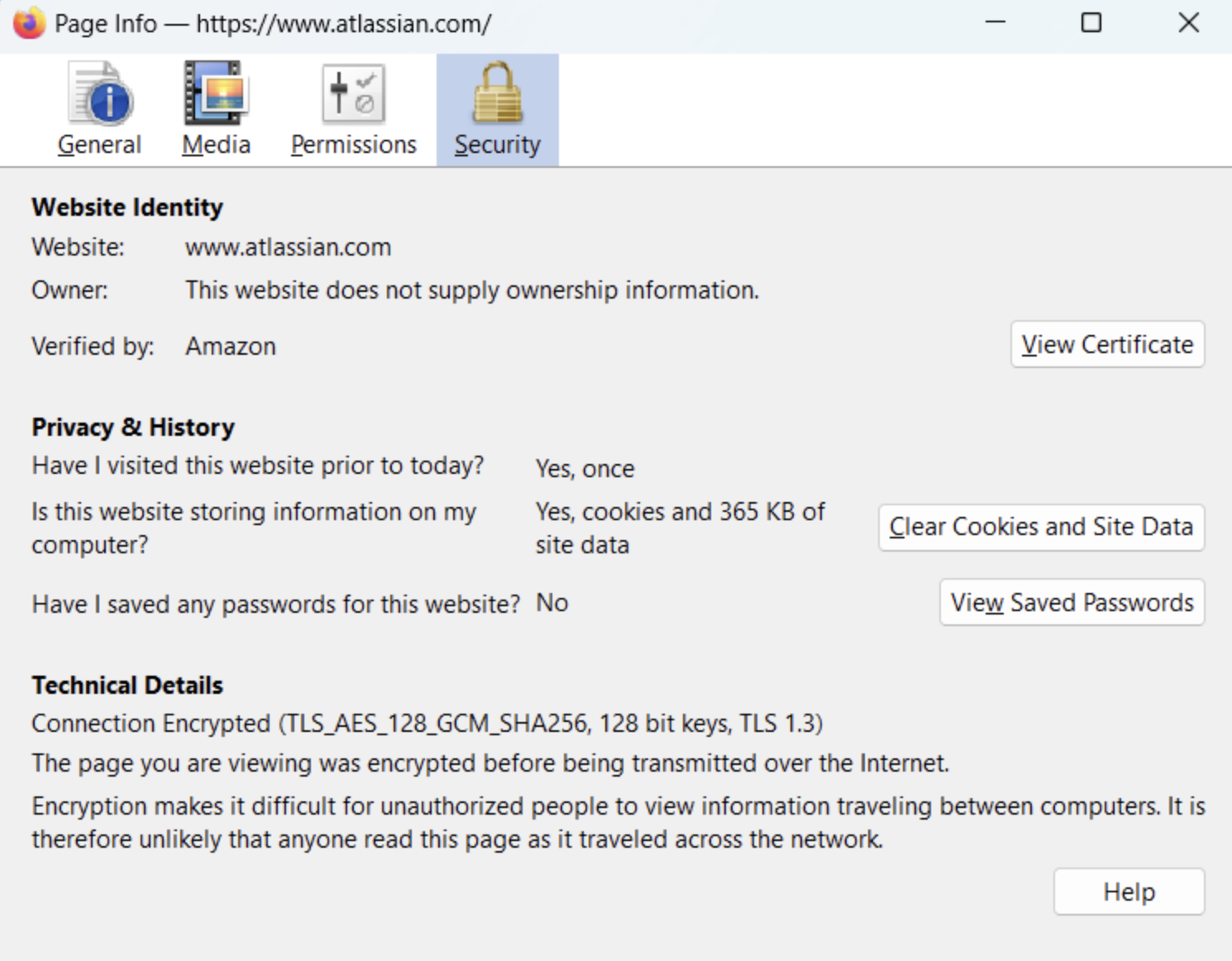
Step 1: Get a self-signed certificate of the remote server
There are multiple ways of exporting the certificate, Either from the Browser or using the OpenSSL command
Get a Certificate using OpenSSL
$ echo | openssl s_client -servername NAME -connect HOST:PORT |\
sed -ne '/-BEGIN CERTIFICATE-/,/-END CERTIFICATE-/p' > certificate.pemGet a Certificate using the Web browser
Step 2: Configure Git to trust the Certificate
For MAC/Linux:
Once the certificate is saved on the client you can instruct your git client to use it to trust the remote repository by updating the local git config:
# Initial clone
GIT_SSL_CAINFO=/path/to/certificate.pem
git clone https://username@git.example.com/scm/repository.git
# Ensure all future interactions with origin remote also work
cd repository
git config http.sslCAInfo /path/to/certificate.pemFor Windows Client:
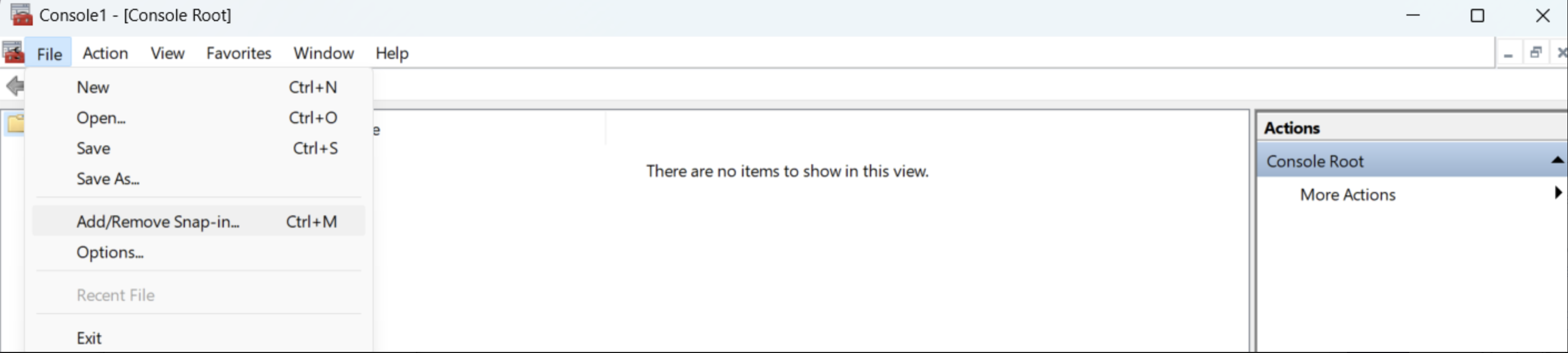
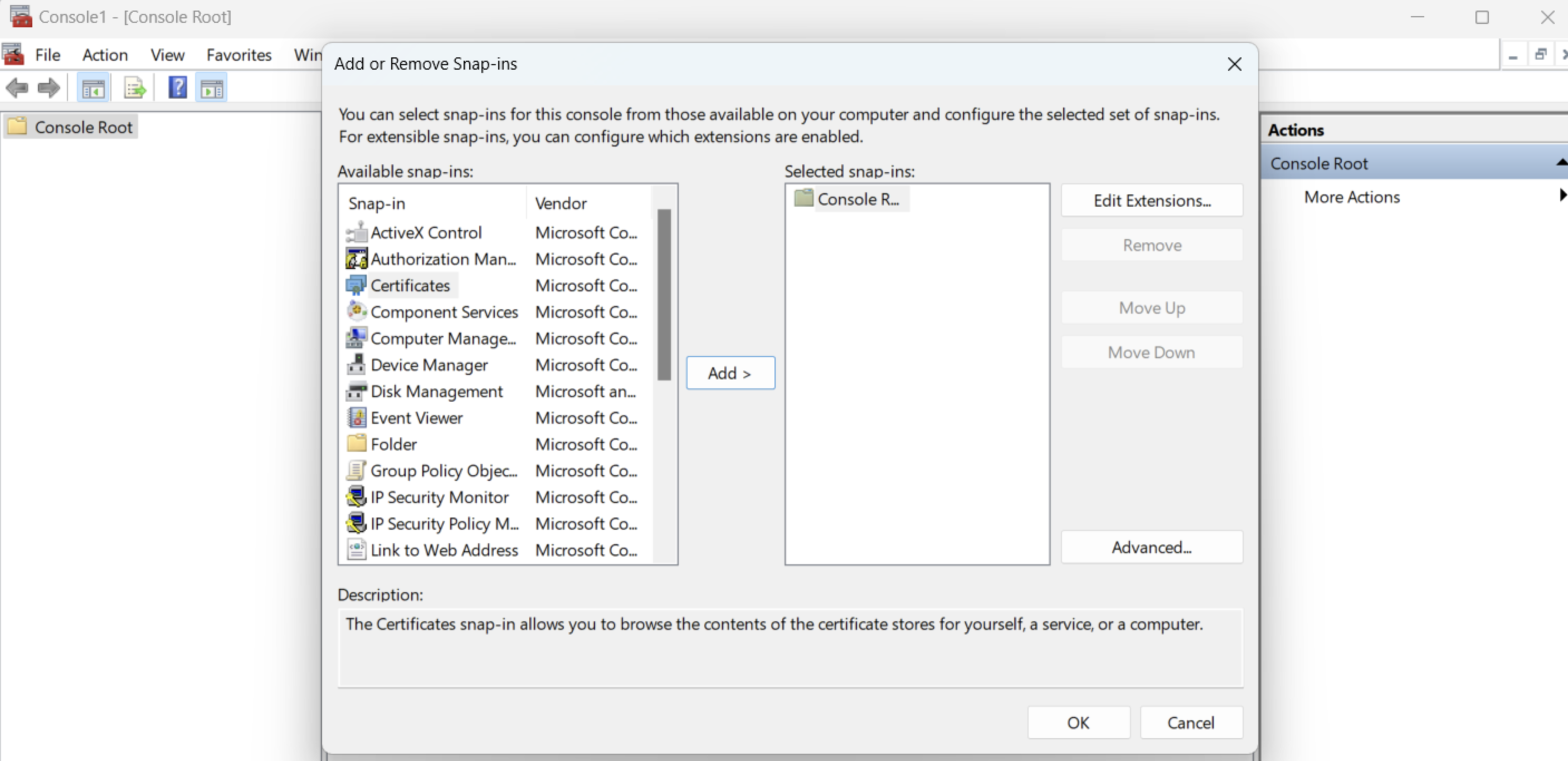
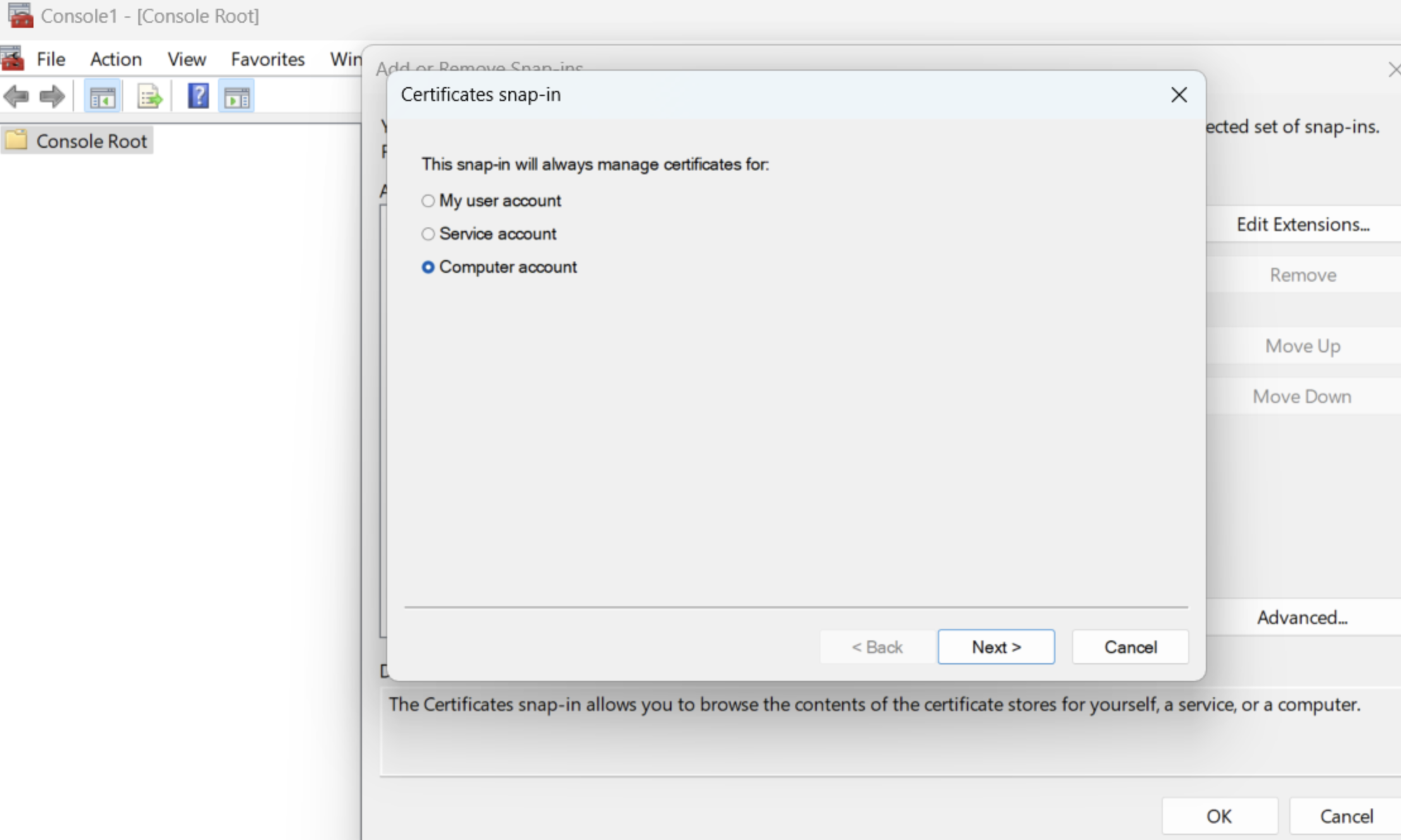
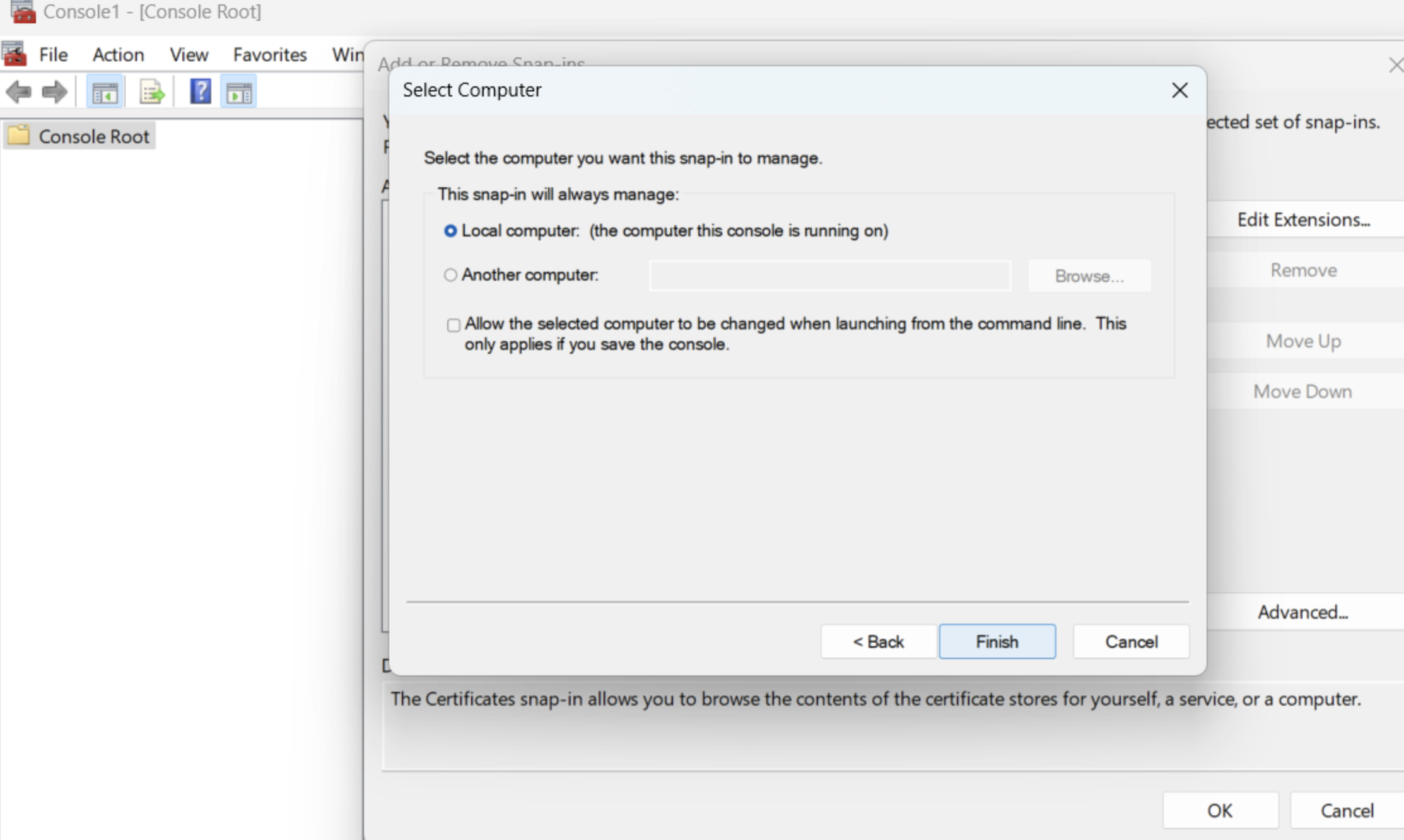
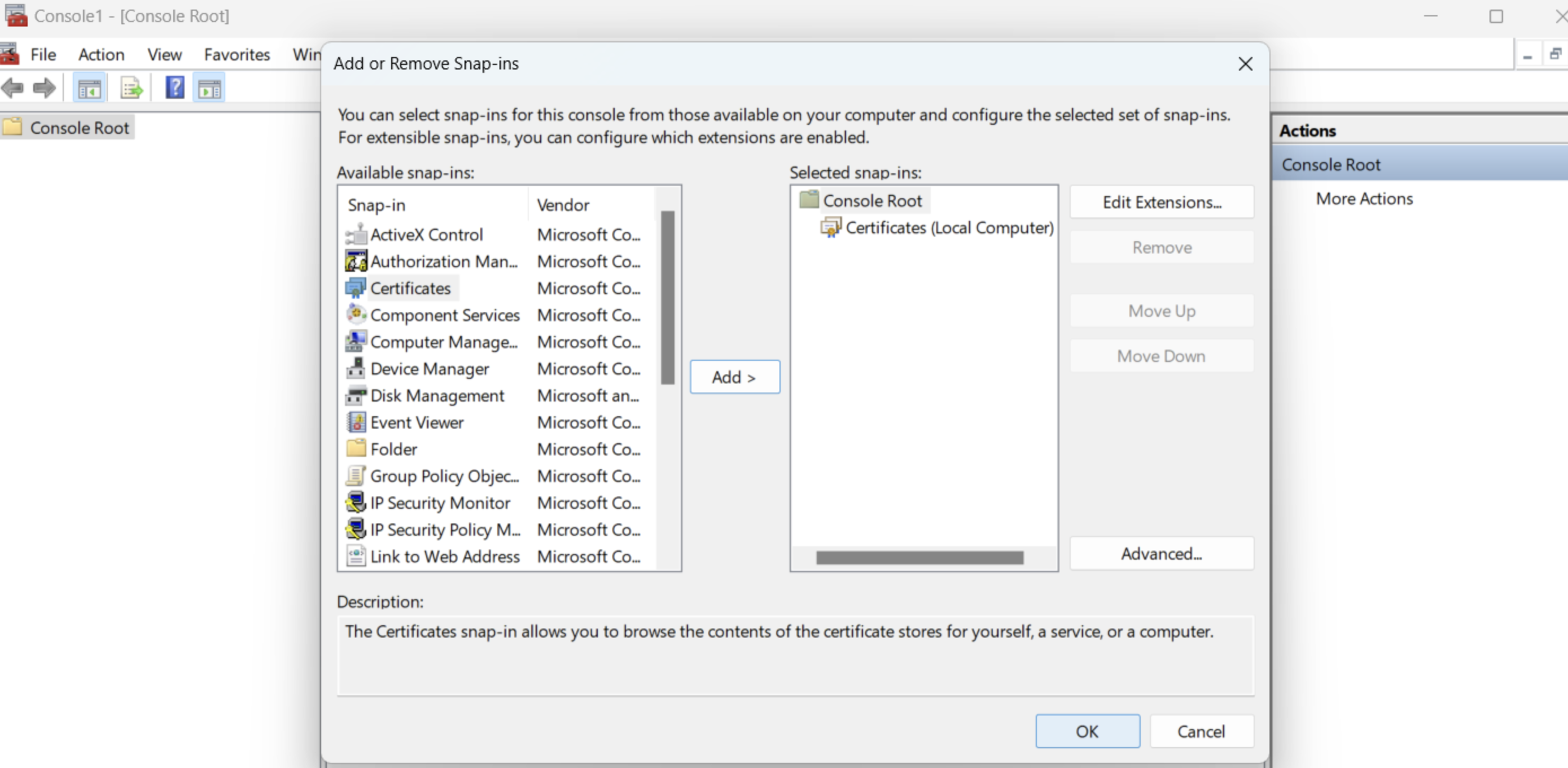
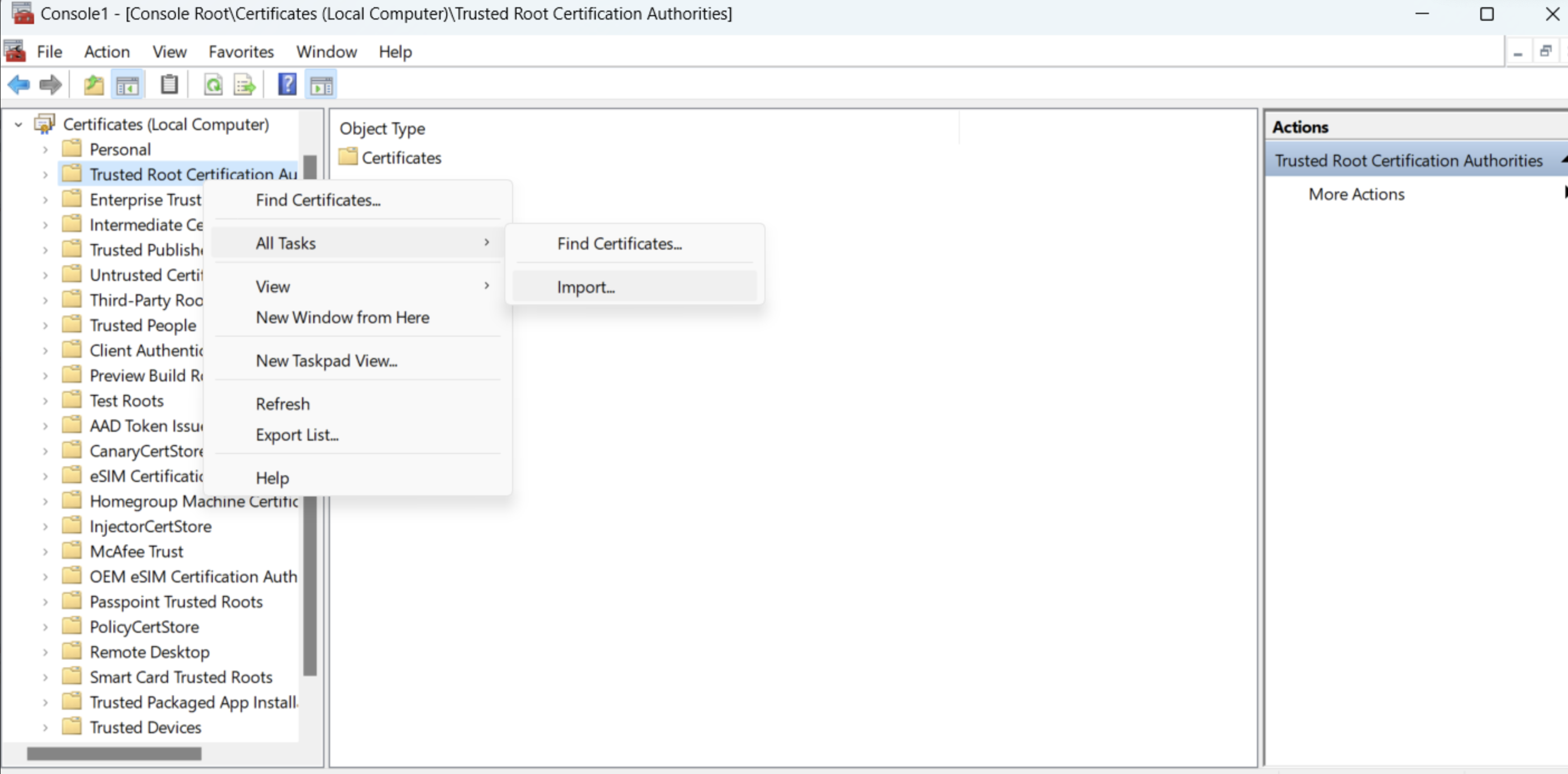
Step 1: Import the certificate into the window trust store
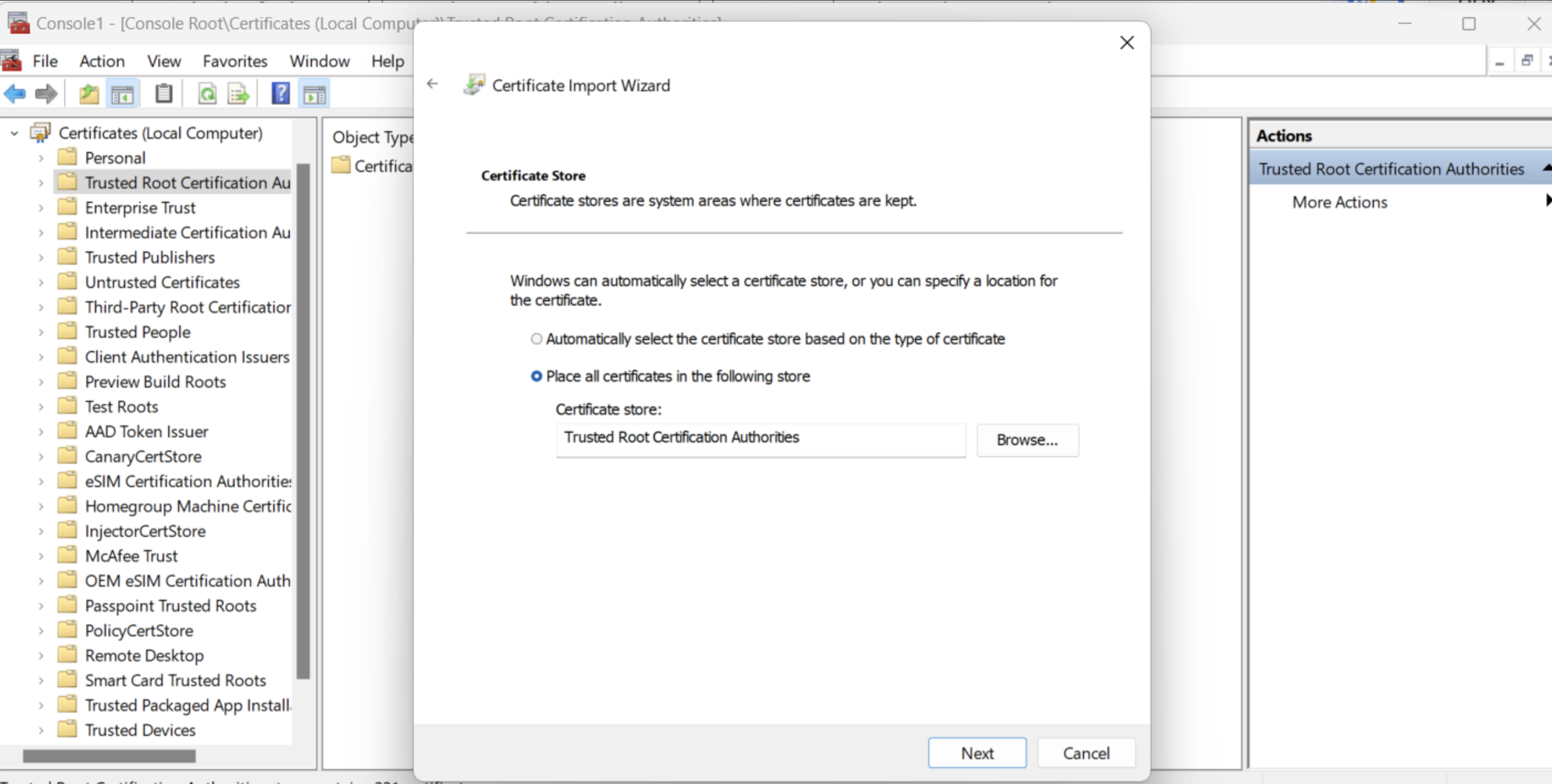
Step 2: Configure git to use the certificate in the Windows Trust store
When using Windows, the problem resides that git by default uses the "Linux" crypto backend. Starting with Git for Windows 2.14, you can configure Git to use SChannel, the built-in Windows networking layer as the crypto backend. To do that, just run the following command in the GIT client:
git config --global http.sslbackend schannelThis means that it will use the Windows certificate storage mechanism and you don't need to explicitly configure the curl CA storage (http.sslCAInfo) mechanism. Once you have updated the git config, Git will use the Certificate in the Windows certificate store and should not require http.sslCAInfo setting.