A sample deployment project
On this page we will examine a sample deployment project, and work through the steps required to get a deployment project up and running.
On this page:
Step 1: Create a deployment project
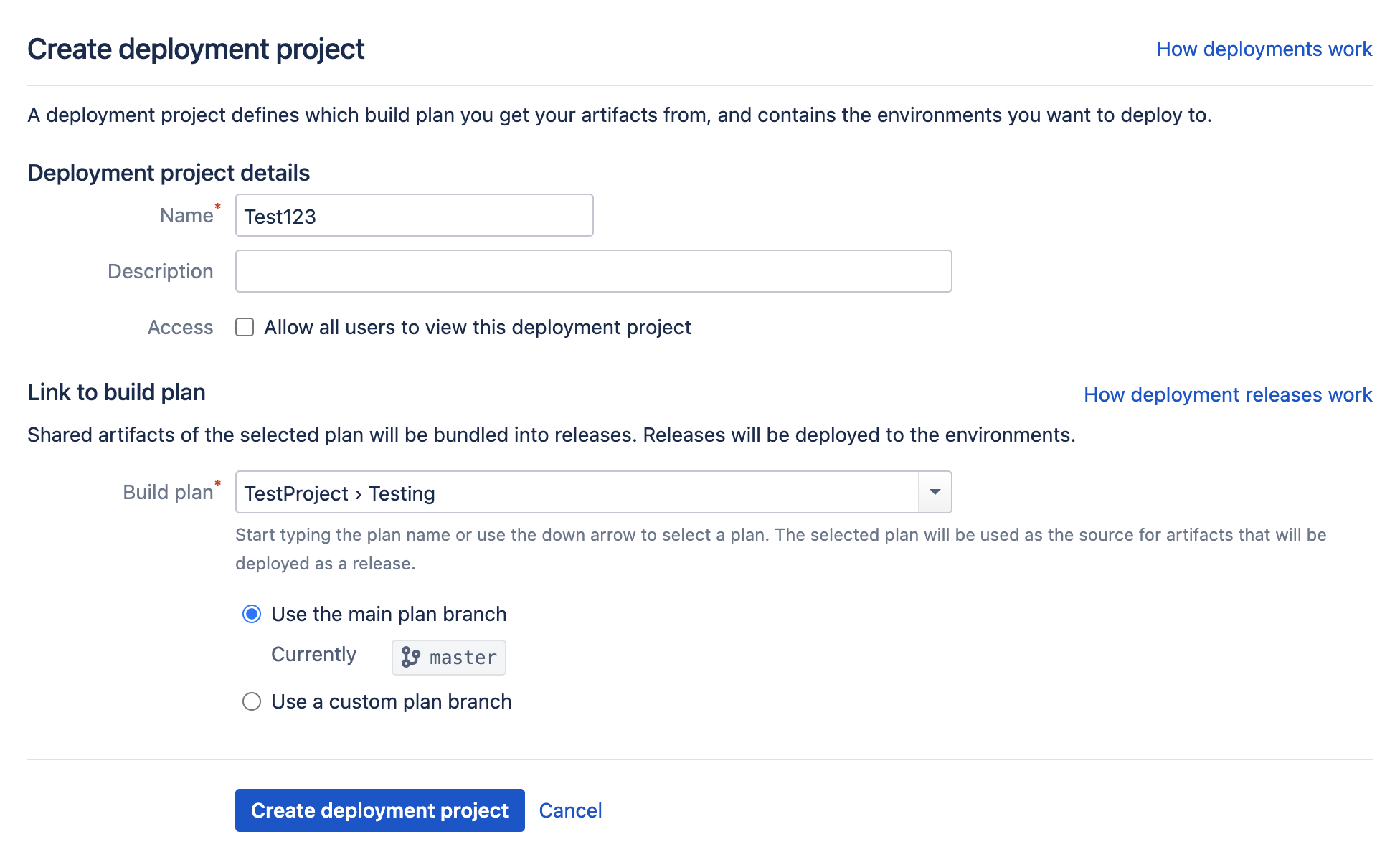
The first step in creating a deployment project is to associate the project with an existing build plan. You can do it at the same time as creating the deployment project. To create a new deployment project, and associate an existing build plan with it:
- Select Create > Create deployment project in the dropdown menu from the top navigation bar.
- Complete the Name and Description fields as required.
- Select an existing build plan in Build plan. Bamboo will identify any relevant build plans in the menu.
- If your build plan has a plan branch, Bamboo will detect it and offer an additional field for completion.
- Select Save deployment project. Your deployment project will be created, and will automatically be associated with the build plan you selected above.
Step 2: Define the release naming scheme
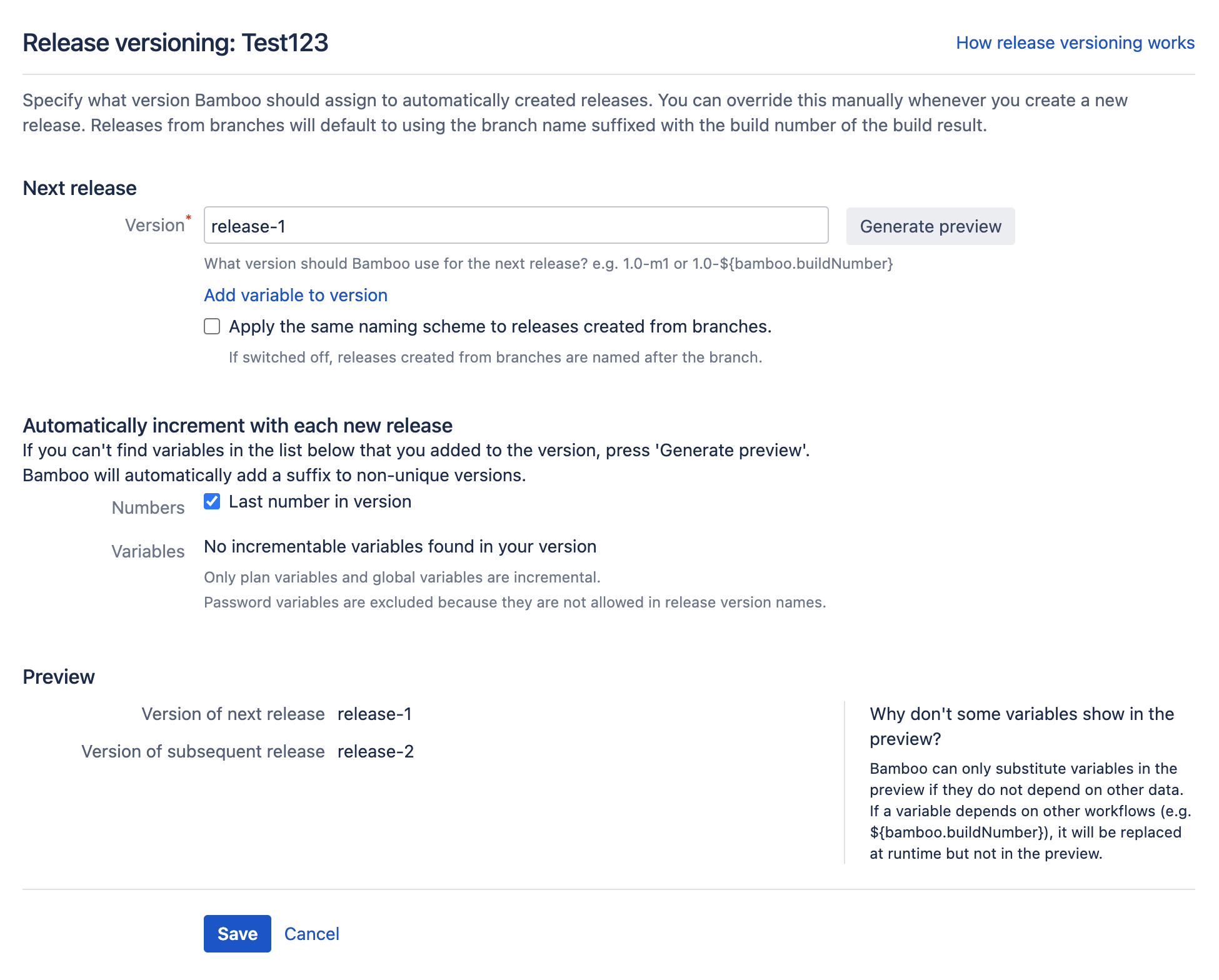
The next step is to provide a version naming strategy for the deployment project. This will define how the deployment project will ascribe names to current and subsequent artifact bundles that it generates. See Naming versions for deployment releases for more information. To configure your version naming scheme:
- From the deployment project configuration screen, select Release versioning.
- Complete the required fields according to your naming scheme. In this example we can see that a simple naming scheme has been adopted - the next name will be release-1, and the subsequent release-2.
- Select Save.
Step 3: Create a deployment environment
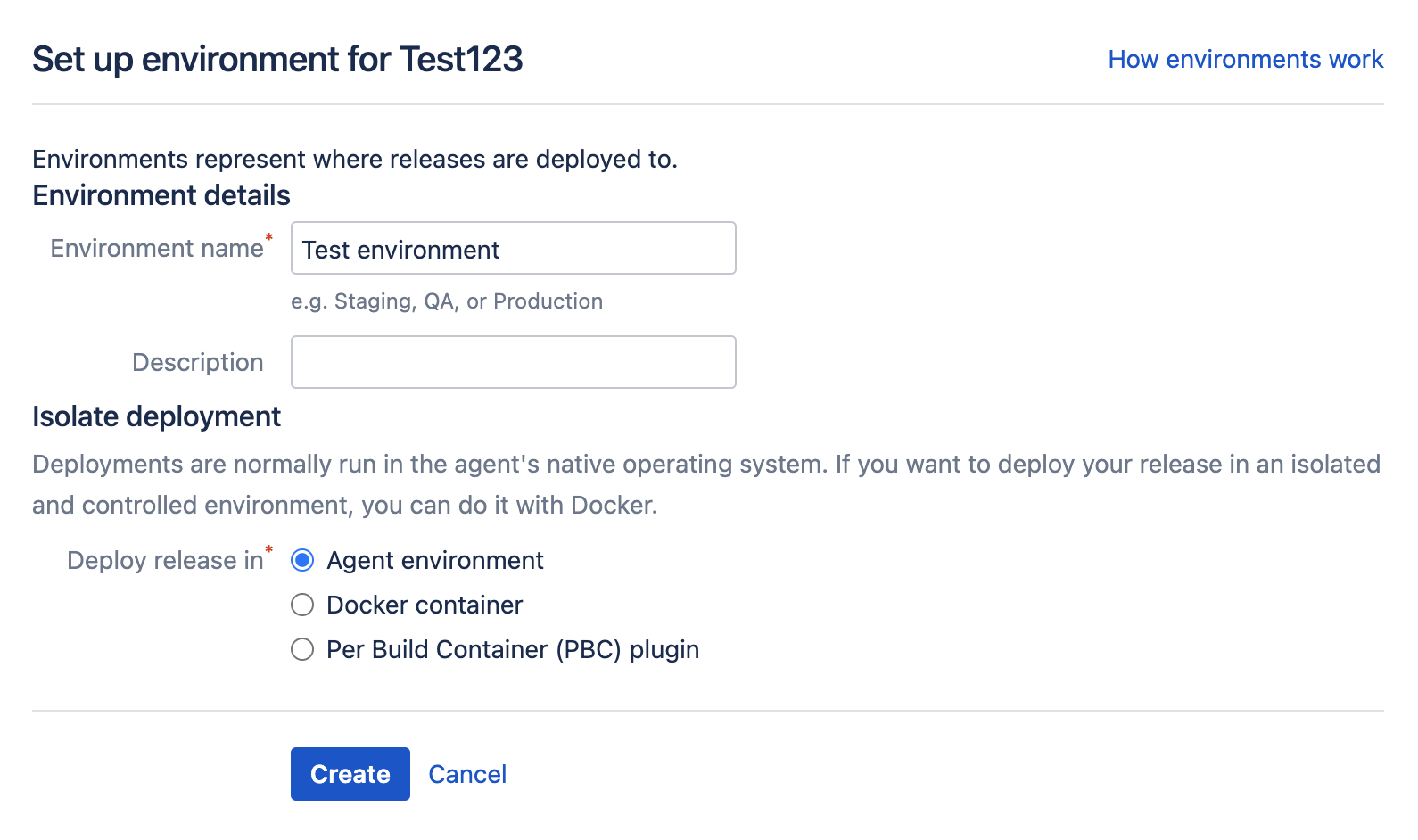
Once we have defined our naming scheme, we need to create a deployment environment for the artifact(s) to be deployed into. Typically, deployment environments include Test, Staging, QA, and Production, however there's no limit to creating useful deployment environments. Let's look at how it's done:
- From the deployment project configuration screen, select Add environment.
- Enter the name of the deployment environment, and a brief description.
- Select Create.
Step 4: Add some environment tasks
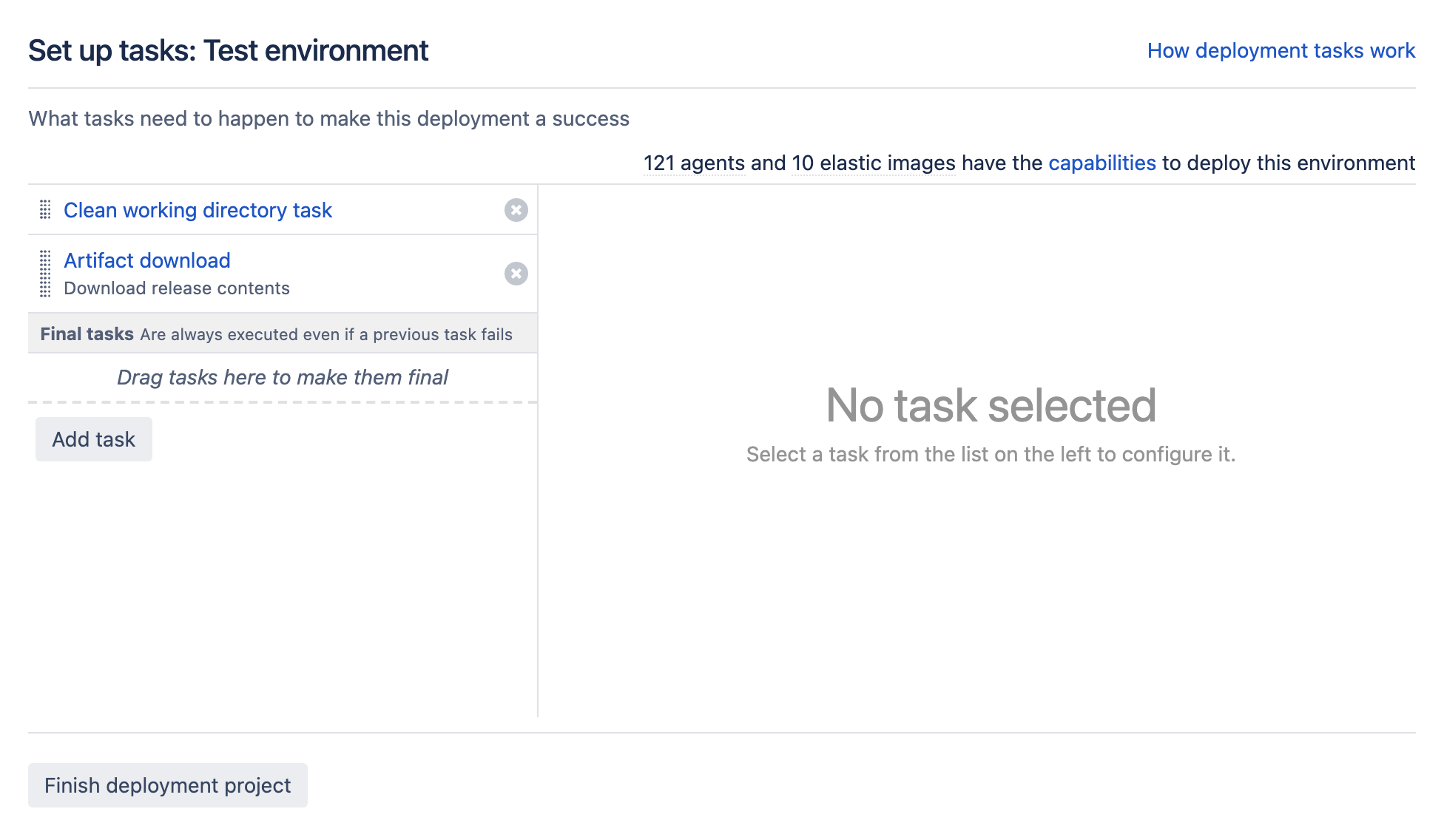
Tasks are activities that the deployment project will perform in order to run. These could be checking out some code from a repository, downloading an artifact from a server, or running a script. Let's have a look at how to add a couple of tasks to the deployment environment:
- From the deployment project configuration screen, select Set up tasks:
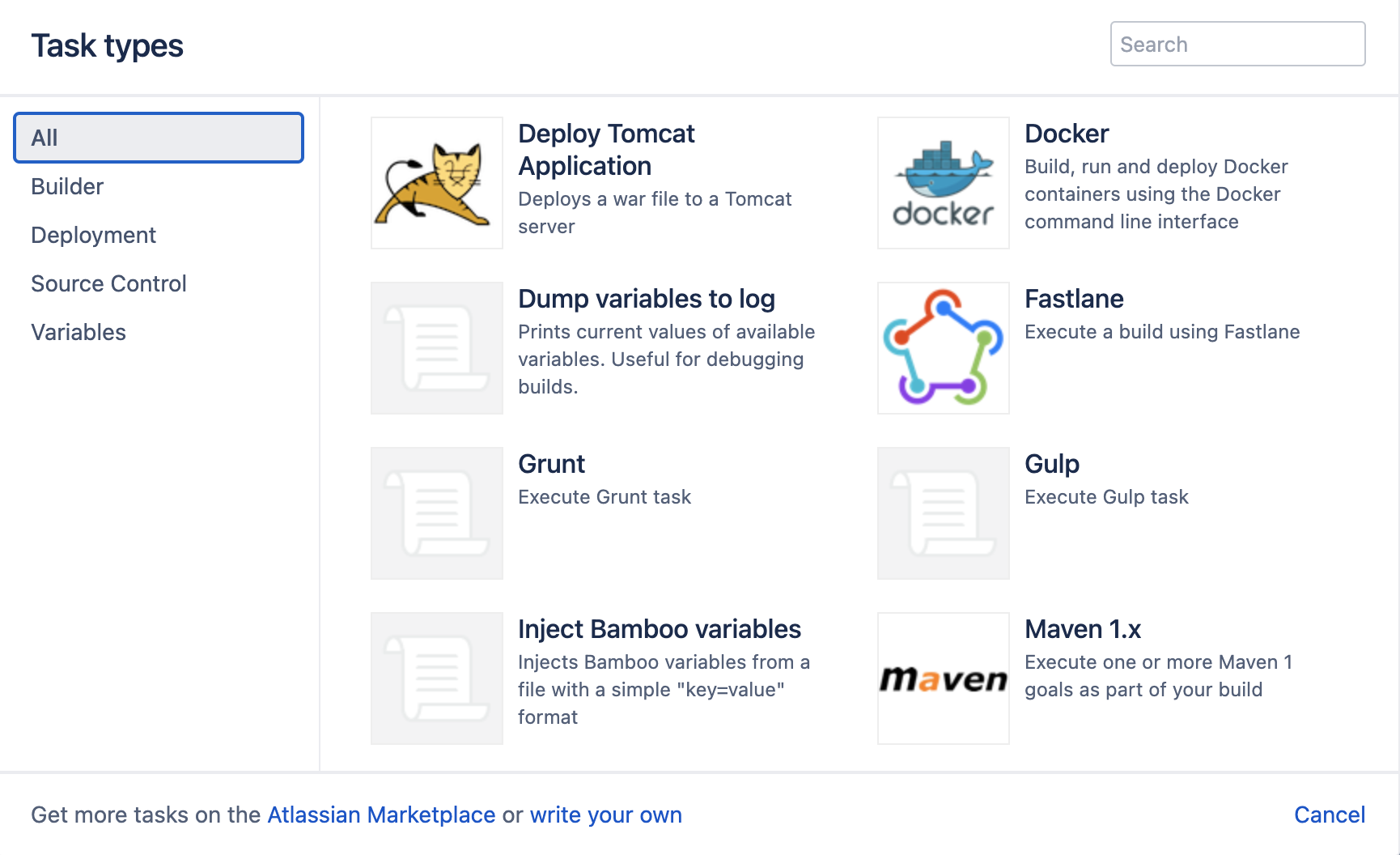
- Select Add task to display the list of tasks that are available to you:
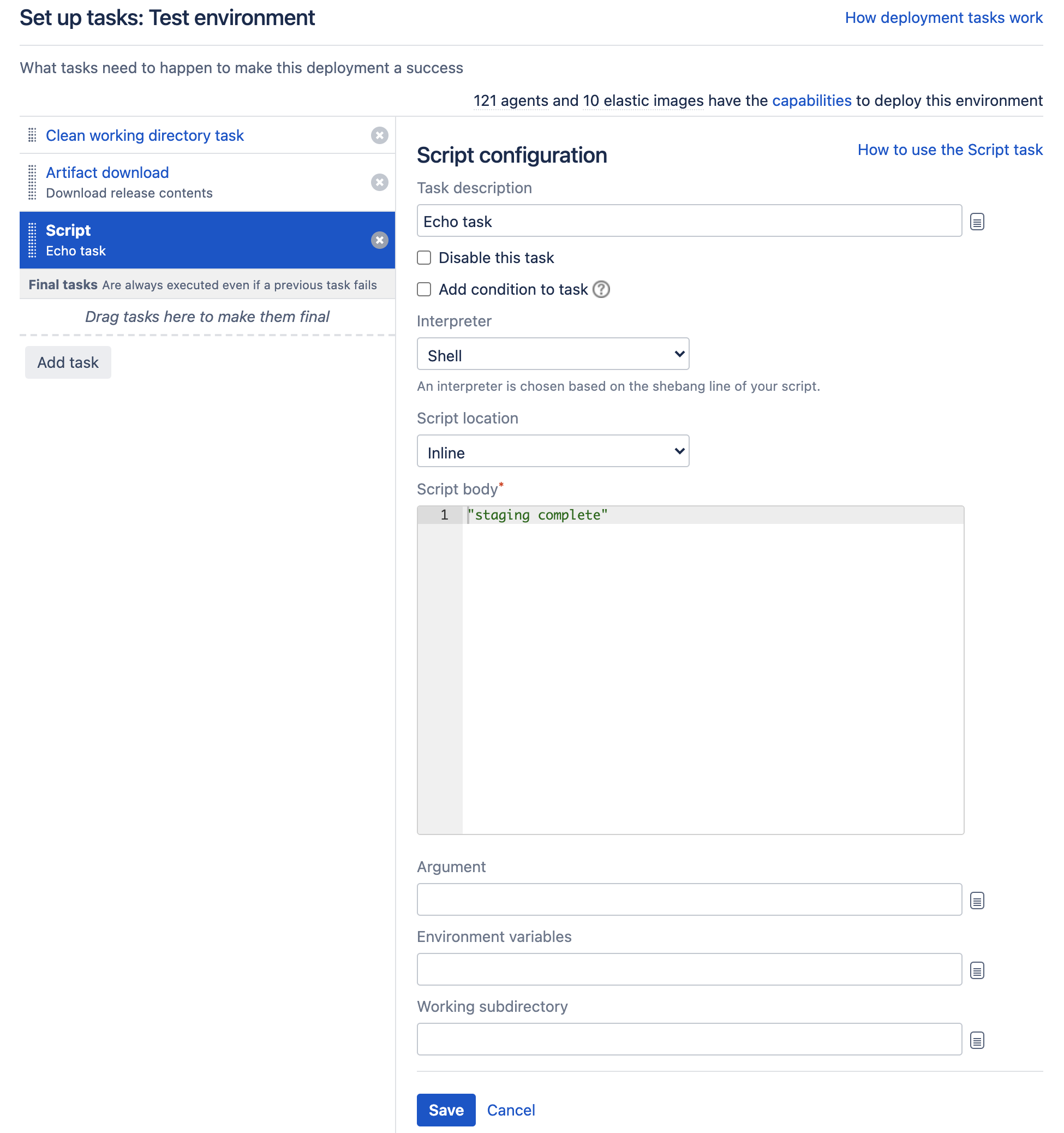
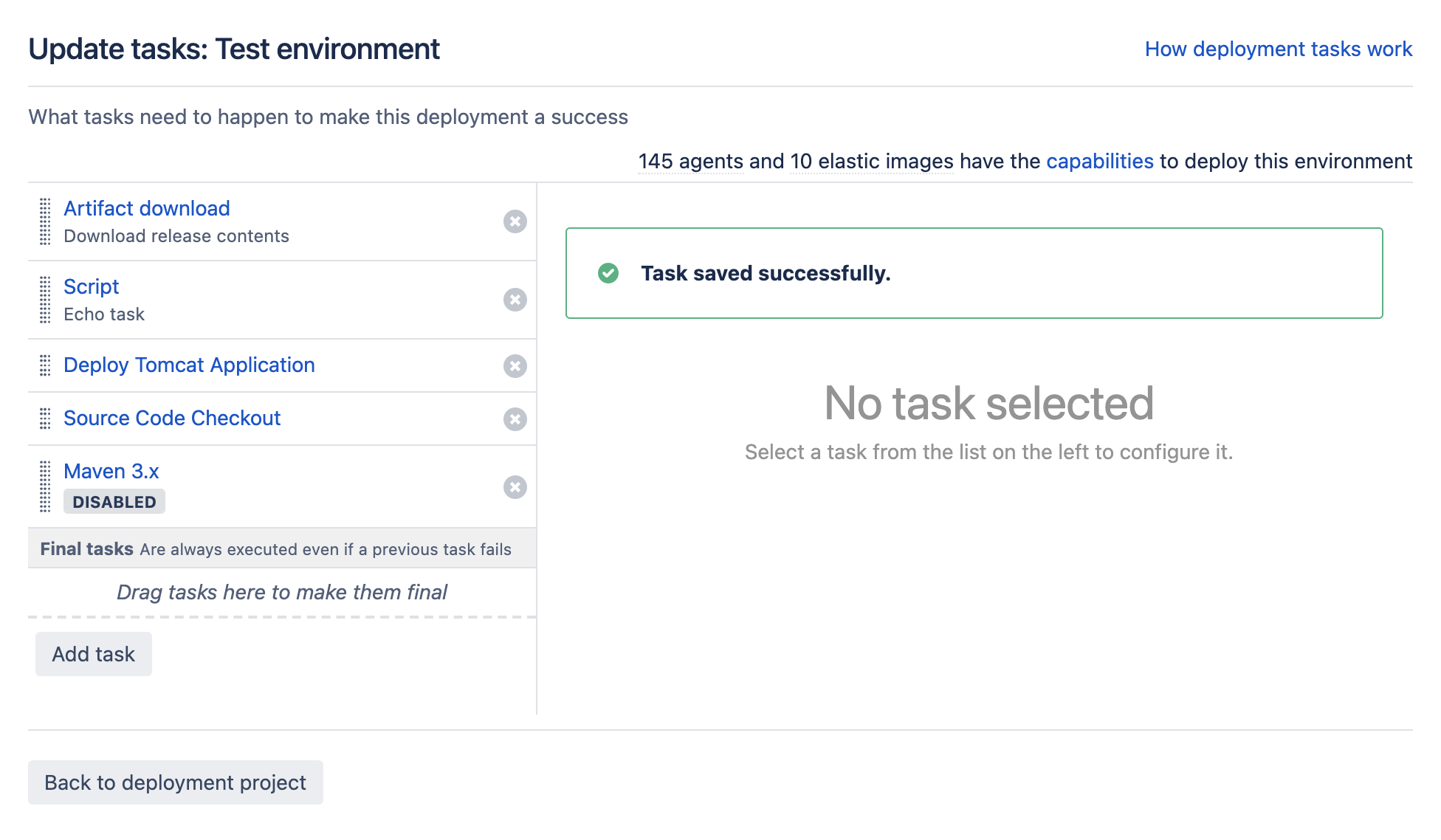
In this example, we will add a simple script task to run as part of our build. Selecting the task we wish to add adds it to the set up tasks screen, and allows us to configure the individual task: - Select Save to save the individual task configuration, and then on Finish deployment project to complete configuration of the script task for the deployment environment. In reality, we would require a number of tasks, not least one to obtain an artifact for use in the deployment. The following task configuration for a production environment includes an artifact download, DB change script, a Tomcat deployment, source code checkout and a Maven 3.x task:
Step 5: Let's deploy!
Our sample deployment project now has all of the elements required to run. We can trigger the deployment project manually by selecting the appropriate deploy () icon on the Deployment projects page.
Step 6: Additional deployment environment options
But deployments don't end here. This simple example is just a snapshot of how a deployment project is configured and works. Bamboo deployment projects feature a host of additional features to help you manage your development and deployment processes. These include:
- Automated triggering - Select to automatically deploy after a successful build plan completes, or at a scheduled time.
- Agents - Assign specific agents, elastic agents, or image configurations to execute the deployment for the environment.
- Variables - Incorporate variables for use when deploying versions to environments.
- Permissions - Define what users are allowed to view, edit, and deploy in the environment.
- Notifications - Define who and how notifications about events for the environment are made.