Configuring Bitbucket with AWS Secrets Manager
AWS Secrets Manager is a service to retrieve credentials through a runtime call, eliminating hard-coded credentials altogether. This type of encryption is especially useful if you want a secure storage option for your database credentials.
AWS Secrets Manager uses AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) for authentication and access control so you don’t need to create tokens or maintain keys with other third parties.
We don’t currently support automated rotating credentials.
To configure Bitbucket to work with AWS Secrets Manager:
Create your secret in AWS Secrets Manager
Check your permissions to retrieve your secret
Authenticate to AWS
Confirm that you can retrieve your secret
Add the secret to the properties file
The following steps will guide you through the process. For additional help with AWS Secrets Manager, visit https://docs.aws.amazon.com/secretsmanager/index.html.
Step 1: Create your secret in AWS Secrets Manager
You can create a secret as plaintext or structured text. Creating a plaintext secret is faster and easier than creating a structured secret.
To see how they differ, check the following example, which shows how each option looks in the AWS console and your code.
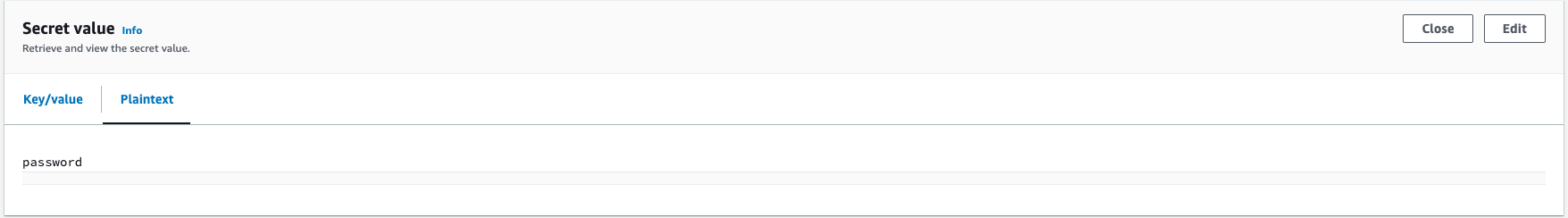
Plaintext secret
AWS console showing a plaintext secret with the name mySecretId:
passwordHow this might appear in your code:
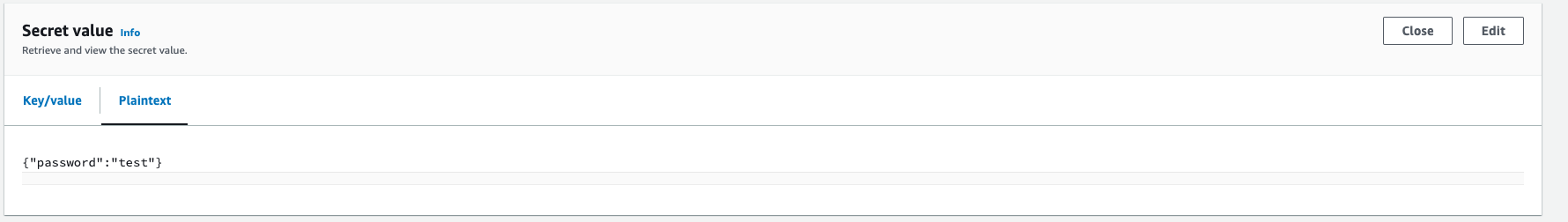
{"region":"ap-southeast-2","secretId":"mySecretId"}Structured secret
AWS console showing a structured secret with the name mySecretId, which has a secretPointer value of password:
{"password": "mySecretPassword"}How this might appear in your code:
{"region":"ap-southeast-2","secretId":"mySecretId", "secretPointer": "/password"}In the example above, the JSON keys include:
| JSON key | Description |
|---|---|
region | The AWS region ID of the secret source. |
secretID | The ID of the secret. |
secretPointer | A JSON pointer for the secret value (required if your secret value is in a key/value pair structure). Note that this value should be prefixed with a slash (/). |
Detailed steps
Ensure you have decided whether to use a plaintext secret or a structured secret (see the content above these steps for further details).
Follow the instructions provided by AWS to create a secret: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/secretsmanager/latest/userguide/create_secret.html
Step 2: Check your permissions to retrieve your secret
To retrieve any secrets from AWS Secrets Manager, Bitbucket must have the appropriate AWS permissions, namely:
secretsmanager:GetSecretValue
Here is a sample Identity and Access Management (IAM) policy providing appropriate permissions (based on a least privilege model):
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/MyRole"
},
"Action": "secretsmanager:GetSecretValue",
"Resource": "arn:aws:secretsmanager:us-west-2:123456789012:secret:1a2b3c"
}
]
}Additional info
For more details on configuring permissions follow the AWS instructions (with linked examples).
If you’re using your own KMS key for secret retrieval permission, follow the AWS instructions (with examples).
Step 3: Authenticate to AWS
Bitbucket uses the AWS SDK for Java 2.x to communicate with AWS Secrets Manager. The SDK will search for credentials in your Bitbucket environment in the predefined sequence below until it can be authenticated.
Amazon EC2 instance profile credentials are recommended by Amazon. If using this option then it is also advisable to use v2 of the Instance Meta Data Service.
- Environment variables
Java system properties
If using Java system properties be aware that these values may be logged by the product on startup.
Web identity token from AWS Security Token Service
The shared credentials and
configfiles (~/.aws/credentials)Amazon ECS container credentials
Amazon EC2 instance profile credentials (recommended by Amazon)
For information on setting credentials in your environment, Amazon has developer guides on Working with AWS Credentials.
Step 4: Confirm that you can retrieve your secret
Now that a secret has been created, the correct permissions are in place and Bitbucket is appropriately authenticated to AWS, let’s confirm the secret can be retrieved.
Run the following command from your host environment:
aws secretsmanager get-secret-value --secret-id=mySecretId --region=ap-southeast-2Step 5: Add the secret to bitbucket.properties
Back up the
<home-directory>/shared/bitbucket.propertiesfile. Move the backup to a safe place outside of your instance.In the
bitbucket.propertiesfile, add or modify theencrypted-property.cipher.classnameproperty to contain:com.atlassian.secrets.store.aws.AwsSecretsManagerStoreIn the
bitbucket.propertiesfile, add or modify thejdbc.passwordproperty to contain the coordinates to the secret in AWS Secrets Manager prefixed with{ENC}:{ENC}{"region":"ap-southeast-2","secretId":"mySecretId", "secretPointer": "/password"}The value is defined as a JSON object with the following values:
region(required) – the AWS region where the AWS secret is locatedsecretId(required) – the name of the secretsecretPointer(optional) – the key containing the password in a secret with the key-value structure. If omitted, the password is treated as plaintext.
Once updated,
bitbucket.propertiesshould contain:encrypted-property.cipher.classname=com.atlassian.secrets.store.aws.AwsSecretsManagerStore jdbc.password={ENC}{"region":"ap-southeast-2","secretId":"mySecretId", "secretPointer": "/password"}Restart Bitbucket.