Working with object types
An object type groups objects that use the same kind of information, conveyed through their common attributes. Rather than a single PC, your object types would be Computers, Hardware, Software, Employees, and so on. And items like PCs or actual employees form objects of that object type. You can create as many different object types as you like, and then group your various objects within. Object types can be whatever you want them to be as Assets is very open and flexible.
Define your object types with attributes
Attributes is what defines your object types (and underlying objects). They work like fields to which you add data—Jira's issue fields would be the best comparison. You'd choose attributes for your object types, and then the same attributes need to be filled in for underlying objects, whenever someone creates them. You can have as many attributes as you need, and they also come in different shapes and sizes: text, dates, references to other objects, statuses, and so on. When you create attributes for objects, you can also link one object type to another.
Here's a sample object type with its attributes:
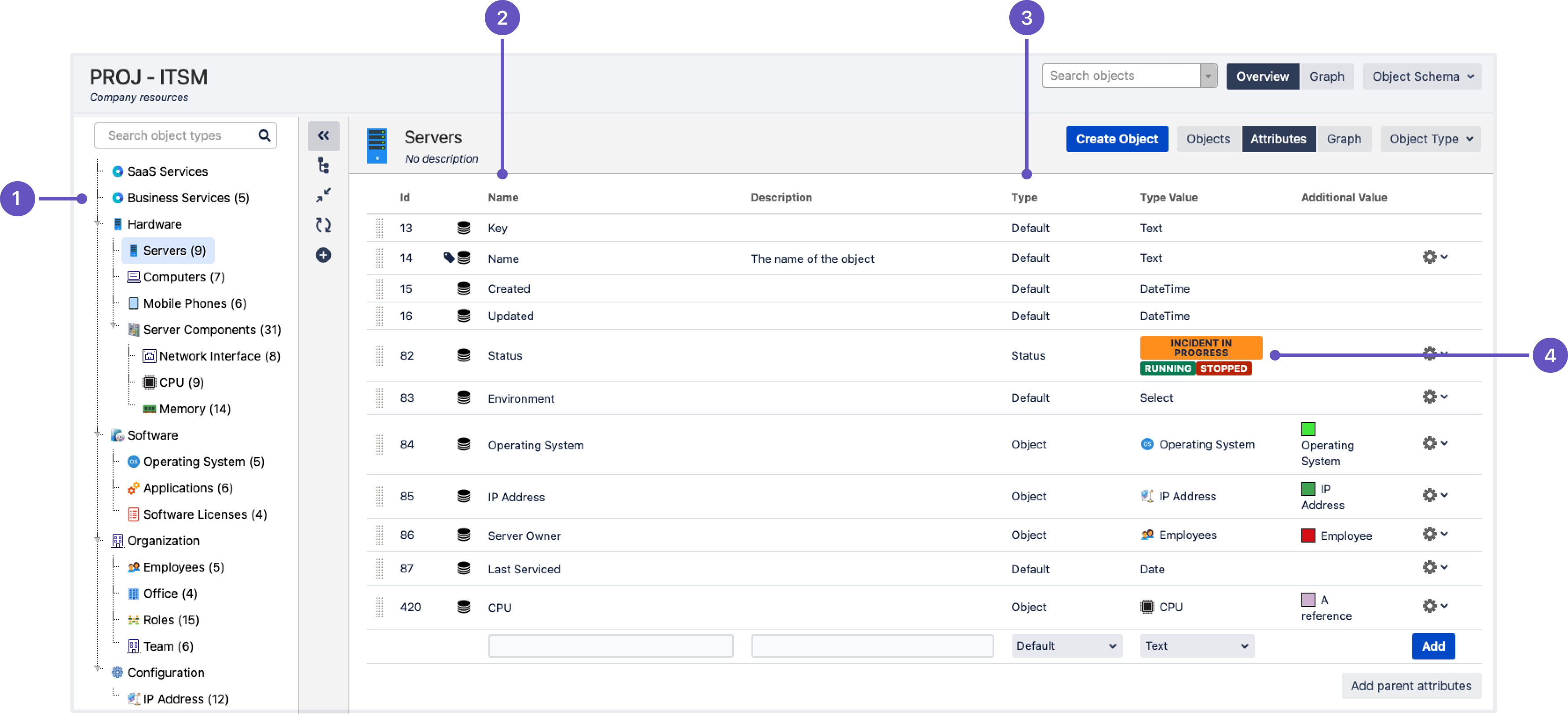
- Object types: List of object types within a schema, with Server selected.
- Attributes: List of attributes configured for this specific object type.
- Type: Type of attributes, here you can see the default ones or object (references to other objects)
- Type and additional value: Extra values that depend on the attribute type. Note statuses – these will change through automation when an incident is raised against one of the underlying servers.
Get started with object types
Here's a list of pages that have all the info you need: