Installing Bamboo Data Center
These instructions are applicable for installing Bamboo Data Center on your own hardware.
This guide covers installing for the first time, with no existing data, or migrating your Bamboo Server to a Data Center instance.
Install Bamboo Data Center on a single node
If your organization doesn't need high availability or disaster recovery capabilities right now, you can install Bamboo Data Center without setting up a cluster.
Deploying Data Center on a single node will be the same as deploying a Server installation, just with a different license. Head to Bamboo installation guide to learn about all the ways in which you can install Bamboo.
Install Bamboo Data Center in a cluster
If your organization requires continuous uptime and disaster recovery, you'll want to run Bamboo Data Center in a cluster.
Before you begin
- See Clustering with Bamboo Data Center for a complete overview of hardware and infrastructure considerations.
- Make sure you environment meets requirements listed in Bamboo Data Center requirements.
Provision the shared database and filesystem nodes
Before you install the first Bamboo application node, you need to provision the shared database and shared filesystem to use with Bamboo Data Center.
1. Download Bamboo
To download Bamboo for your operating system, go to download page.
2. Create the installation directory
Extract the downloaded file to an install location.
The path to the extracted directory is referred to as the
<Bamboo installation directory>in these instructions.
3. Provision your shared database
Set up your shared database server.
Ensure your database is configured to allow enough concurrent connections.
See Connecting Bamboo Server to an external database for more information, and note that clustered databases are not supported.
4. Provision your shared file system
You’ll need to create a remote directory that is readable and writable by all nodes in the cluster. There are multiple ways to do this, but the simplest is to use an NFS share.
On your file server, ensure that NFS is configured with enough server processes. For example, some versions of Red Hat Enterprise Linux and CentOS have a default of 8 server processes. If you use either distribution, you may need to edit your /etc/sysconfig/nfs file, increase the value of RPCNFSDCOUNT, and restart the nfs service.
5. Create the local and shared home directories
Bamboo node should have access to 2 folders it uses for files storage: local and shared.
The shared folder is shared between all cluster nodes and used to keep artifacts and other build results. The local home is used to keep node-specific files. The local home should not be accessible by other nodes.
Specify your Bamboo home directories before you run Bamboo for the first time.
Create your Bamboo home directories (without spaces in the name).
You should not create your Bamboo home directory inside the Bamboo installation directory — they should be entirely separate locations. If you do put the home directory in the Bamboo installation directory, it will be overwritten, and lost, when Bamboo is upgraded.
6. Configure file share mount
On each cluster node, mount the shared home directory as ${BAMBOO_HOME}/shared . Note that only the ${BAMBOO_HOME}/shared directory should be shared between cluster nodes. All other directories, including ${BAMBOO_HOME} should be node-local (that is, private to each node).
You can configure a custom location for you home shared folder. Also, when using multiple nodes, you must define a path to a shared home location. See Configuring shared home location.
7. Synchronize system clocks
Ensure all your cluster nodes have synchronized clocks and identical timezone configuration. Here are some examples for how to do this:
8. Configure Bamboo home settings
- Open
<Bamboo installation directory>/atlassian-bamboo/WEB-INF/classes/bamboo-init.properties. - Uncomment the following lines:
- bamboo.home
- bamboo.shared.home
- Provide the absolute path to the
${BAMBOO_HOME}and${BAMBOO_SHARED_HOME}directories.Example:
bamboo.home=/var/bamboo/bamboo-home bamboo.shared.home=bamboo-san:/bamboo-shared
9. Start the first cluster node installation
Start Bamboo instance and provide your Bamboo Data Center license. If you need a Bamboo Data Center license, you can purchase one that fits your needs, or, get an evaluation license. Then provide necessary DB connection settings and admin user credentials.
Install and configure your load balancer
Step 1. Configure protocols and health checks on your load balancer
Your load balancer must proxy the following protocols:
Protocol | Typical port on the load balancer | Default port on the Bamboo cluster nodes | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
HTTP | 80 | 8085 | HTTP mode. Session affinity ("sticky sessions") should be enabled using the 52-character BAMBOOSESSIONID cookies. |
HTTPS | 443 | 8085 | HTTP mode. Terminating SSL at the load balancer and running plain HTTP to the Bamboo cluster nodes is highly recommended. |
TCP | 54663 | 54663 | TCP mode. For remote agents JMS connection. To prevent communication failure, the Load Balancer should be configured to SSL Passthrough the request from the remote agents to Bamboo server. |
Your load balancer must support session affinity ("sticky sessions") using the BAMBOOSESSIONID cookie. Bamboo Data Center assumes that your load balancer always directs each user's requests to the same cluster node. If it does not, users may be unexpectedly logged out or lose other information that may be stored in their HTTP session.
When choosing a load balancer, it must support the HTTP, HTTPS, and TCP protocols. Note that:
Apache does not support TCP mode load balancing.
HAProxy versions older than 1.5.0 do not support HTTPS.
Your load balancer must support health checks of the cluster nodes. Configure it to perform a periodic HTTP GET of http://<bamboo>:8085/rest/api/latest/status, where <bamboo> is the cluster node's name or IP address. This returns one of two HTTP status codes:
200 OK
500 Internal Server Error
If a cluster node does return 200 OK within a reasonable amount of time, the load balancer should direct traffic to it.
You should then be able to navigate to http://<load-balancer>/, where <load-balancer> is your load balancer's name or IP address. This will take you to your Bamboo Server front page.
2. Configure Bamboo Server proxy settings
You must include these details in the Connector tag in every node of <bamboo-installation-folder>/conf/server.xml:
<Connector
...
proxyName="<INSERT THE LOAD BALANCER URL>"
proxyPort="80"
scheme="http"
>
...
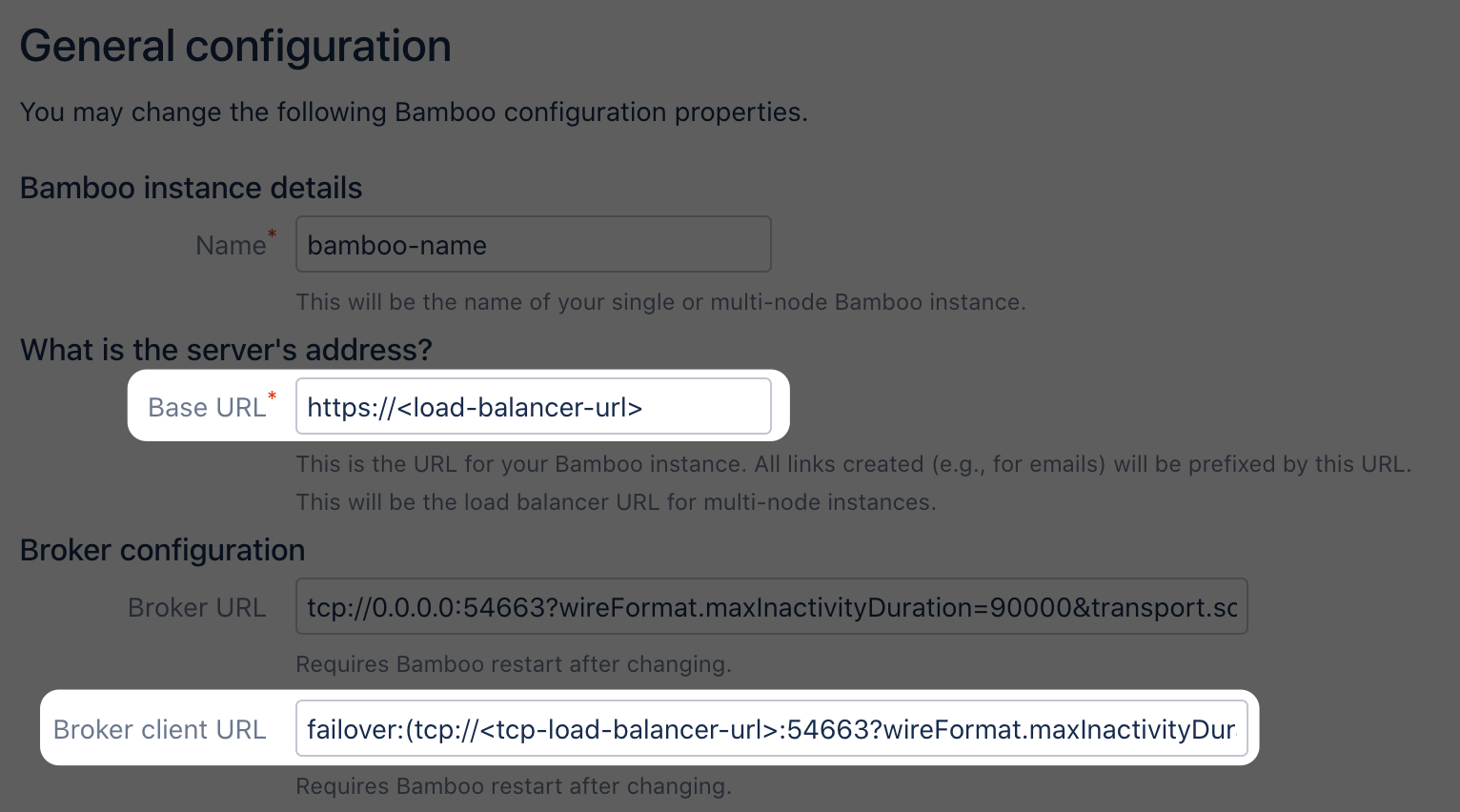
</Connector>3. Change base-url and client-broker-url
- In Bamboo, go to > System > General configuration.
- Set the Base URL and broker client URL.
4. Add a new Bamboo application node to the cluster
On the second node, create an empty Bamboo home directory and mount it in the same location as the Bamboo home directory on the first node.
Don’t copy the contents of the Bamboo home directory from the first node to the second node. Bamboo will automatically populate its home directory on the first startup
- Copy the whole Bamboo installation directory from the first node to the same location on the second node.
- Copy the
bamboo.cfg.xmlfile from the root of the Bamboo local home directory on the first node to the same location on the second node. Start Bamboo on the second node.
Check the logs to verify that the instance on the second node was able to connect to the database, create the local home folders, and wait for lock acquisition.
5. Connect the new Bamboo cluster node to the load balancer
If you are using your own hardware or software load balancer, consult your vendor's documentation on how to add the new Bamboo cluster node to the load balancer.
If you are using HAProxy, in your haproxy.cfg file uncomment the following lines:
server bamboo2 192.168.0.2:8085 check cookie bamboo2server bambooTcp2 192.168.0.2:54663 check port 54663and restart haproxy:
sudo service haproxy restartCongratulations!
That's it! Bamboo Data Center is accessible under the following URL: http://<load-balancer-url>:<port>