Connect Bamboo to a PostgreSQL database
This page describes how to connect Bamboo to a PostgreSQL database.
Note that the JDBC driver for PostgreSQL is bundled with Bamboo. You do not have to download and install the driver.
See Supported platforms for other information about the versions of PostgreSQL supported by Bamboo.
On this page:
1. Configuring PostgreSQL
Accept remote TCP connections (remote PostgreSQL server only)
If you are connecting Bamboo to a remote PostgreSQL server (i.e. if your PostgreSQL server is not installed locally on your Bamboo server host system), you will need to configure your data/postgresql.conf and data/pg_hba.conf files to accept remote TCP connections from your Bamboo server's IP address.
The following PostgreSQL documentation contains information on the appropriate listen_addresses value in the postgresql.conf file as well as the pg_hba.conf file:
PostgreSQL 13 documentation — Connections and Authentication
PostgreSQL 14 documentation — Connections and Authentication
PostgreSQL 15 documentation — Connections and Authentication
PostgreSQL 16 documentation — Connections and Authentication
Once you have modified your data/postgresql.conf and data/pg_hba.conf files, you will need to restart PostgreSQL for your changes to take effect.
Creating a Bamboo database
sudo -s -H -u postgres
# Create the Bamboo user:
/opt/PostgreSQL/8.3/bin/createuser -S -d -r -P -E bamboouser
# Create the bamboo database:
/opt/PostgreSQL/8.3/bin/createdb -O bamboouser bamboo
exit
Creating a completely empty Bamboo database is recommended. Avoid using templates to create the database as some may insert default tables which can lead to conflicts when setting up Bamboo.
2. Connecting Bamboo to PostgreSQL
Bamboo provides two ways to connect to a PostgreSQL database — using JDBC or using a datasource. JDBC is generally simpler and is the recommended method.
Run the Setup wizard
For both methods, run the Setup Wizard and choose the Custom Installation option.
On the 'Choose a Database Configuration' page, choose External Database, select PostgreSQL 8.2 and above from the list and click Continue.
Choose one of the following:
Connecting using JBDC
On the 'Database Configuration' page of the Setup Wizard, ensure that Direct JDBC connection has been selected and make the following settings:
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Driver Class Name | Type org.postgresql.Driver (if different from the default). |
| Driver Class Name | Type the URL where Bamboo will access your database (if different from the default). For details about syntax, please refer to the Postgres JDBC driver documentation. |
| User Name | Type the username that Bamboo will use to access your database. |
| Password | Type the password (if required) that Bamboo will use to access your database. |
| Overwrite existing data | Select if you wish Bamboo to overwrite any tables that already exist in the database. |
Screenshot 1: Setup JDBC Connection (PostgreSQL)
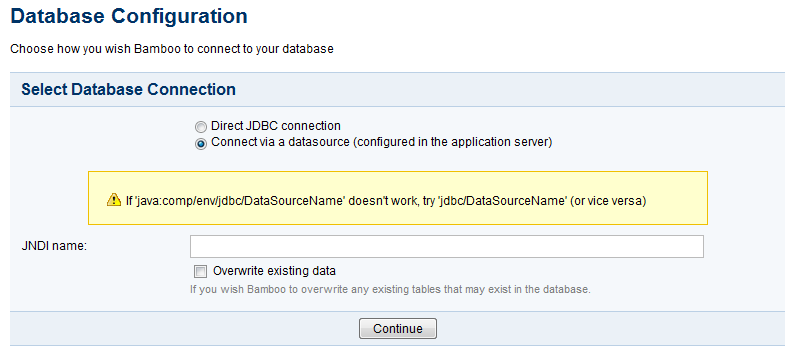
Connecting with a datasource
Configure a datasource in your application server (consult your application server documentation for details).
For details about the syntax to use for the JDBC database URL, please see the Postgres JDBC driver documentation.
On the 'Database Configuration' page of the Setup Wizard, choose Connect via a datasource (configured in the application server) and make the following settings:
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| JNDI name | Type the JNDI name of your datasource, as configured in your application server.java:comp/env/jdbc/DataSourceName does not work, try jdbc/DataSourceName (and vice versa). |
| Overwrite existing data | Select if you wish Bamboo to overwrite any tables that already exist in the database. |
Screenshot 2: Setup Datasource Connection