PowerShell is not recognized as an internal or external command
Platform notice: Server and Data Center only. This article only applies to Atlassian products on the Server and Data Center platforms.
Support for Server* products ended on February 15th 2024. If you are running a Server product, you can visit the Atlassian Server end of support announcement to review your migration options.
*Except Fisheye and Crucible
Summary
A Script Task from a deployment or build plan may fail with the following error:
PowerShell is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file
Environment
Bamboo (or its agents) running on Windows OS.
Diagnosis
If your Bamboo version is 6.10.2 or older, please beware of the following bug:
However, if you're running a more recent version of Bamboo, or you also experience this issue when running the PowerShell command directly from Windows' Command Prompt, please proceed with the below.
Cause
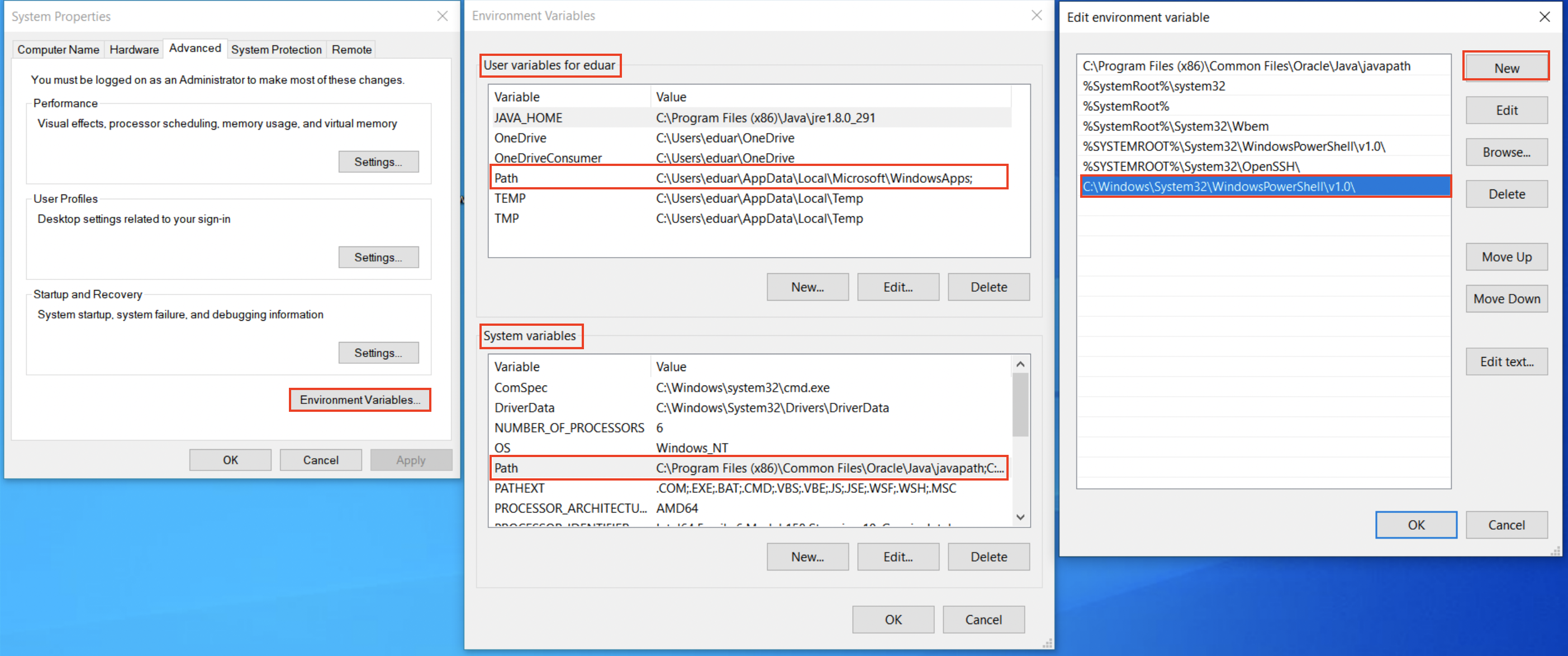
This is caused by the user (or system) PATH environment variable not containing the directory where the PowerShell executable resides. It's usually located at C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe, and although the PATH variable contains the C:\Windows\System32 directory, Windows may have trouble locating the executable within its subfolders.
Solution
The solution consists of adding the directory where the PowerShell executable resides to the PATH environment variable.
- Search for "environment variables" in the Windows search bar and open the respective Control Panel item.
- A System Properties window will appear. Click on "Environment Variables" at the bottom.
- Edit the PATH environment variable and add the path to the folder where PowerShell is located.
- For the changes to be picked up, the agent needs to be restarted. You may also need to restart the machine so all of the other Windows portions pick up the new variable.