Running Confluence Data Center on a single node
Data Center allows you to run Confluence in a cluster with multiple nodes, or on a single server (also known as non-clustered, or standalone Data Center).
This page outlines the architecture and requirements of a non-clustered Confluence Data Center deployment, as well as some of the benefits and considerations.
Architecture
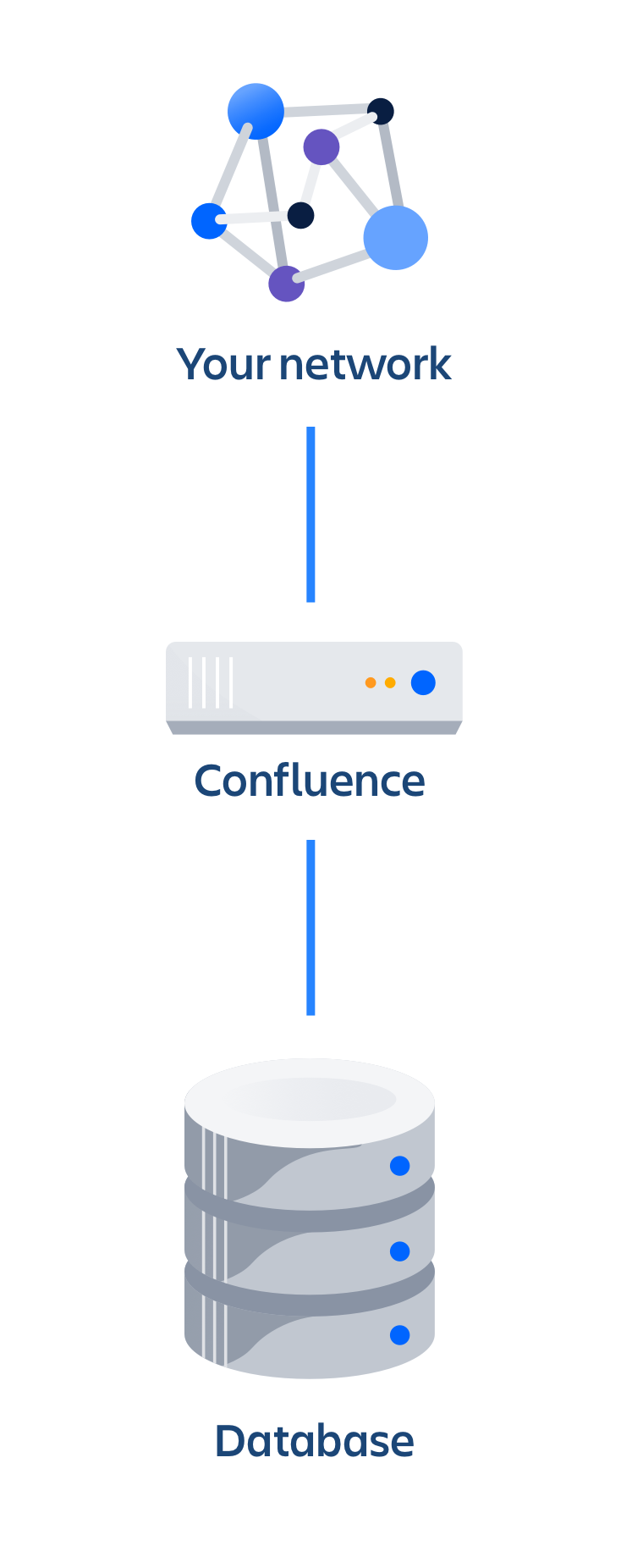
The deployment architecture of a non-clustered Data Center deployment typically looks like this:
As you can see, Confluence Data Center deployed on a single node looks consists of:
- Confluence Data Center running on a single node
- A database that Confluence reads and writes to
See Getting started as a Confluence administrator to learn more about single server Confluence installations.
Requirements
Check our Confluence System Requirements guide for a full overview of the supported platforms and hardware you’ll need.
Non-clustered Confluence Data Center installations have the same minimum requirements as running a Server installation, which was available in versions older than Confluence 8.6.0.
Benefits of running a non-clustered Data Center deployment
There are a range of reasons you may choose a single node Data Center. Some of the benefits include:
- Keeping your existing infrastructure
Running on a single node means that you can upgrade from Server to Data Center without adding to your infrastructure. In most cases, moving to Data Center will be as simple as updating your license. - Accessing Data Center-only features
Your Data Center license unlocks a suite of additional security, compliance, and administration features to help you easily manage enterprise-grade Confluence site – like SAML single sign-on, advanced permission management, rate limiting, and more.
As non-clustered Confluence Data Center installations are cluster-compatible, you can still enable and configure clustering whenever you’re ready to scale. Learn more about setting up a cluster.
Considerations
Some deployments start to experience performance or stability issues once their size profile hits Large or XLarge. Most clustered deployments provide you the flexibility to scale up your infrastructure to address heavy loads (or even scale down to save costs during light loads). On AWS or Azure, you can also quickly address most stability issues by replacing misbehaving nodes with fresh ones.
For more information about size profiles, see Data Center performance – sizing. We also explain our own strategies for managing our clustered deployments in How Atlassians monitor their enterprise deployments.