Setting up SLAs
Good service is what keeps customers coming back and a key ingredient of good service is responsiveness.
With Jira Service Management, you can keep your team on track by setting goals for how quickly you manage customer issues. If these goals are set by your customer contracts, you might know them as Service Level Agreements, or SLAs.
SLAs track the progress of things like:
- Respond to all requests within 2 hours.
- Resolve high-priority requests within 24 hours.
See How teams see SLAs for a detailed look at the Agent's view in different scenarios.
On this page:
How to set SLAs
Your Jira admin or Project admin can set SLAs in Project settings > SLAs.
When you set an SLA, you choose two things:
- A time metric, which defines how and when time will be measured
- A goal, which defines the target to be met
Set a time metric
The time metric works like a stopwatch, tracking the time between two points in an issue's lifecycle. For example, you might start time when an issue is created, pause time while you wait for the customer to respond, and stop time when the issue is resolved.
Jira Service Management has pre-configured time metrics to cover the most common IT requirements, but you can modify these or create your own as needed.
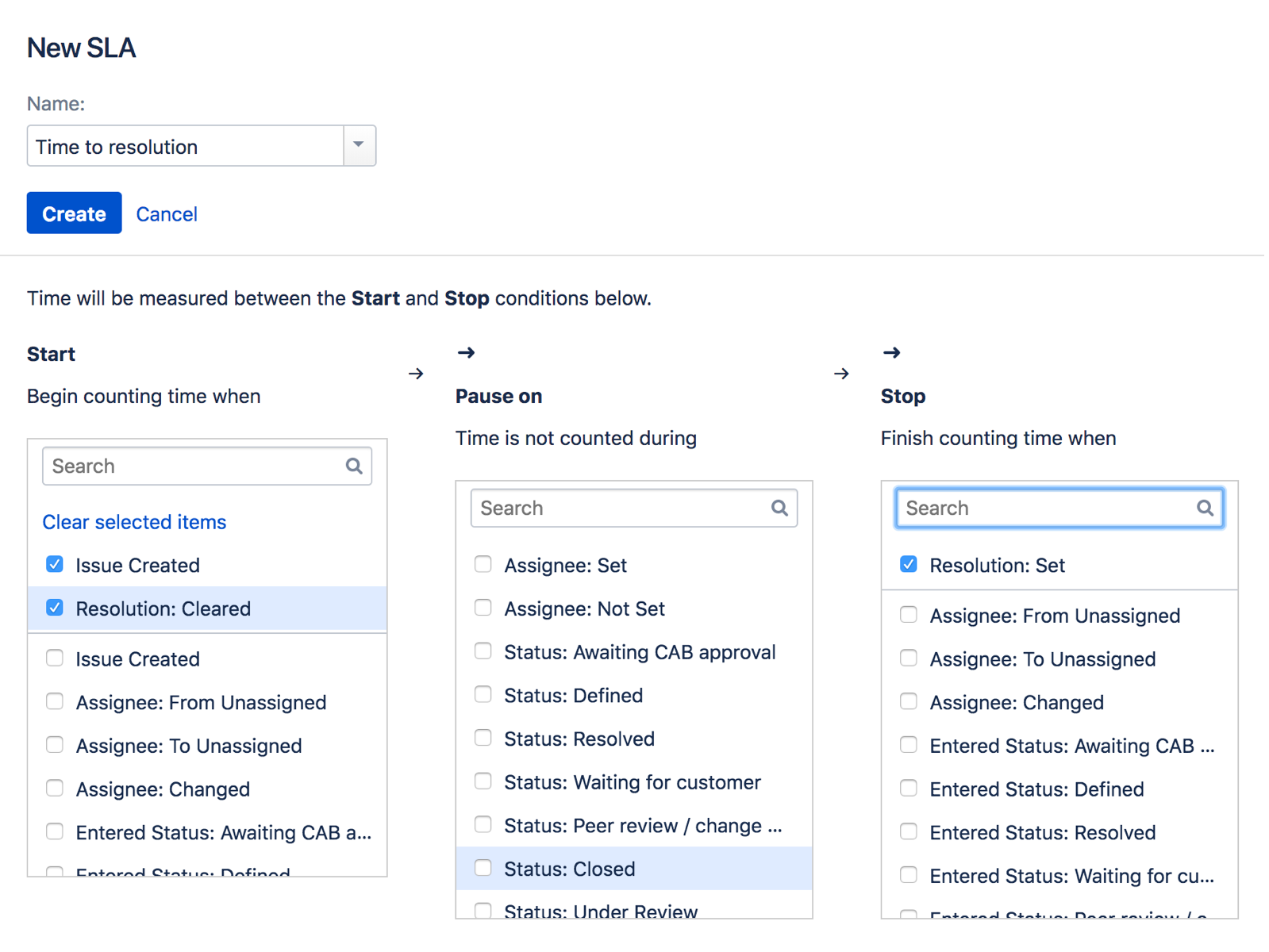
To create a new metric, from your service desk project sidebar, select Project settings > SLAs > Create SLA and fill in the following conditions:
| Condition | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | This name (for example Time to resolution) will appear to agents in the SLAs section of issues. Agents should be able to read the name and know what they’re being measured on. You can't change the name of an SLA metric after you've saved it. |
| Start | Time starts being counted against the SLA when any of these occur (for example, Issue Created). |
| Pause on | Time doesn't get counted against the SLA when at least one of these conditions apply to the issue (for example, Status: Waiting for Customer). |
| Stop | Time stops being counted against the SLA when any of these occur (for example, Resolution: Set). |
You can set multiple conditions for the start, stop, and pause time. Here's an example of the conditions set for the Time to resolution SLA.
Check out Example: creating an SLA with multiple cycles to learn how to create a more complex SLA by starting and stopping the time counter throughout the workflow.
Set a goal
In the Goals section of the SLA metric, choose the type of issue you want to track (Issues), how quickly you want to resolve it (Goal), and your team’s working hours (Calendar).
Here are some examples of goals you might set:
- Resolve blocker issues within 24 hours.
- Resolve blocker issues created by the Build Engineering team within 12 hours.
- Resolve blocker issues created by the Accounting team within 36 hours.
In the New SLA or Edit SLA screen, fill out the following fields to define a goal:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Issues | You can enter specific issue criteria using Jira Query Language (JQL). Base goals on criteria that remain relatively constant throughout an issue's lifecycle (for example, an issue's priority rather than its workflow status). |
| Goal | This is where you specify the target time for the SLA conditions you previously set. When specifying SLA goals that use a fraction of an hour, write the time as Xh Ym (for example, 3h 30m). You can write SLA goals as hours and minutes, but not days. |
| Calendar | The calendar allows you to specify working hours when time can be counted against SLAs. |
You can drag goals in order of importance. An issue is tracked against the first goal criteria it matches on the list:
Set your working hours
Jira Service Management lets you create calendars that match the working hours of your team including lunch breaks, holidays, and weekends. You can then assign that calendar to an SLA, so the clock stops when your team are away.
Read Create and edit SLA calendars to learn how to do this.
SLA calendars are unique to each service project. See Example: Creating a basic SLA for an example of setting up an SLA that uses a 9-5 working day SLA calendar.
How to manage SLA data
If you create a new name for an SLA, it creates a new custom field that is available to all service projects in your Jira site. As a Jira administrator, you can choose whether users have to be Project administrators or Jira administrators to create new SLA names. You can also view the number of SLA fields being used, and clean up unused fields.
To manage these settings:
- Choose Administration () > Applications. Scroll down to the Jira Service Management section and choose Configuration.
- In the SLA metric names section, you can change who can create new SLA metric names. If there are SLA custom fields not in use, click Clean up to delete them.
Best practice SLA usage
- Try to choose an Assignee who's not the Reporter of an issue. If you assign the same user, your SLA might work incorrectly.
- If you edit an existing SLA, Jira Service Management will re-index all the existing issues in the project. For ongoing SLAs, the data for elapsed time will be recalculated to measure against the new metrics, but we won’t recalculate the cycles that have already been completed (i.e. a request fulfilled the Start and Stop conditions).
- If issue data changes in such a way that the goals for the issue change (for example, the priority changes from Critical to Blocker), the time against the previous goal will be tracked against the new goal, for open issues only.
For example, if the Support team spent an hour on a Critical issue, when the issue is escalated to Blocker, the hour still counts against the new goal, even if it causes the SLA to be breached. - If you're using filters in your service project to track SLA data, specifically priorities, make sure these filters include all the priorities defined in the associated priority scheme. See Associating priorities with projects for more details.
- We do not recommend setting up a goal to be dependent on a different SLA.