Content Index Administration
The search index is used by search, the dashboard, some macros, and all the other places where we show information about content in your Confluence site. The search index is made up of:
- a content index which contains content such as the text of pages, blog posts, and comments
- a change index which contains data about each change, such as when a page was last edited.
These indexes are updated automatically as people get work done on your site. Changes, such as a new page, comment, or edit to an existing page, aren't updated in each index immediately. They're placed into queues and regularly processed in batches (as often as every 5 seconds).
View the index queues
It can take a while for the queues to process if there are thousands of changes to your site within a short period.
To check the contents of the queue:
- Go to Administration > General Configuration > Content Indexing.
- Select the Content queue or Change queue tab.
Here you can see the number of items in the queue, the last time the queue was processed, and how long it took to process. This information is useful for troubleshooting if your users report issues with search, dashboard activity feeds.
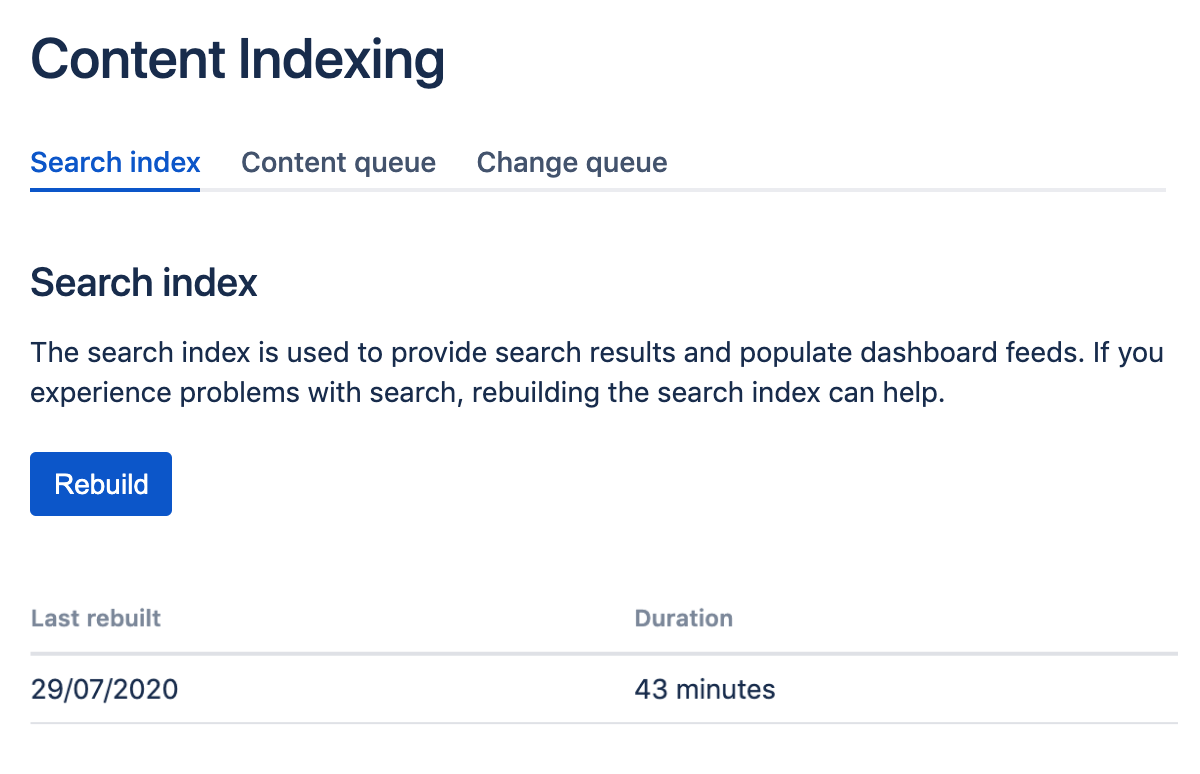
Rebuild the search index
There are some circumstances where you may need to reindex your site, for example, if your users report issues with search, dashboard activity feeds, or if directed to as part of an upgrade.
To rebuild the search index:
- Go to Administration > General Configuration > Content Indexing.
- Select Rebuild and follow the prompts to confirm you want to rebuild the index.
This will rebuild content index and the change index, and can take some time for very large sites.
Screenshot: The Content Indexing screen showing information about the last time the index was rebuilt.
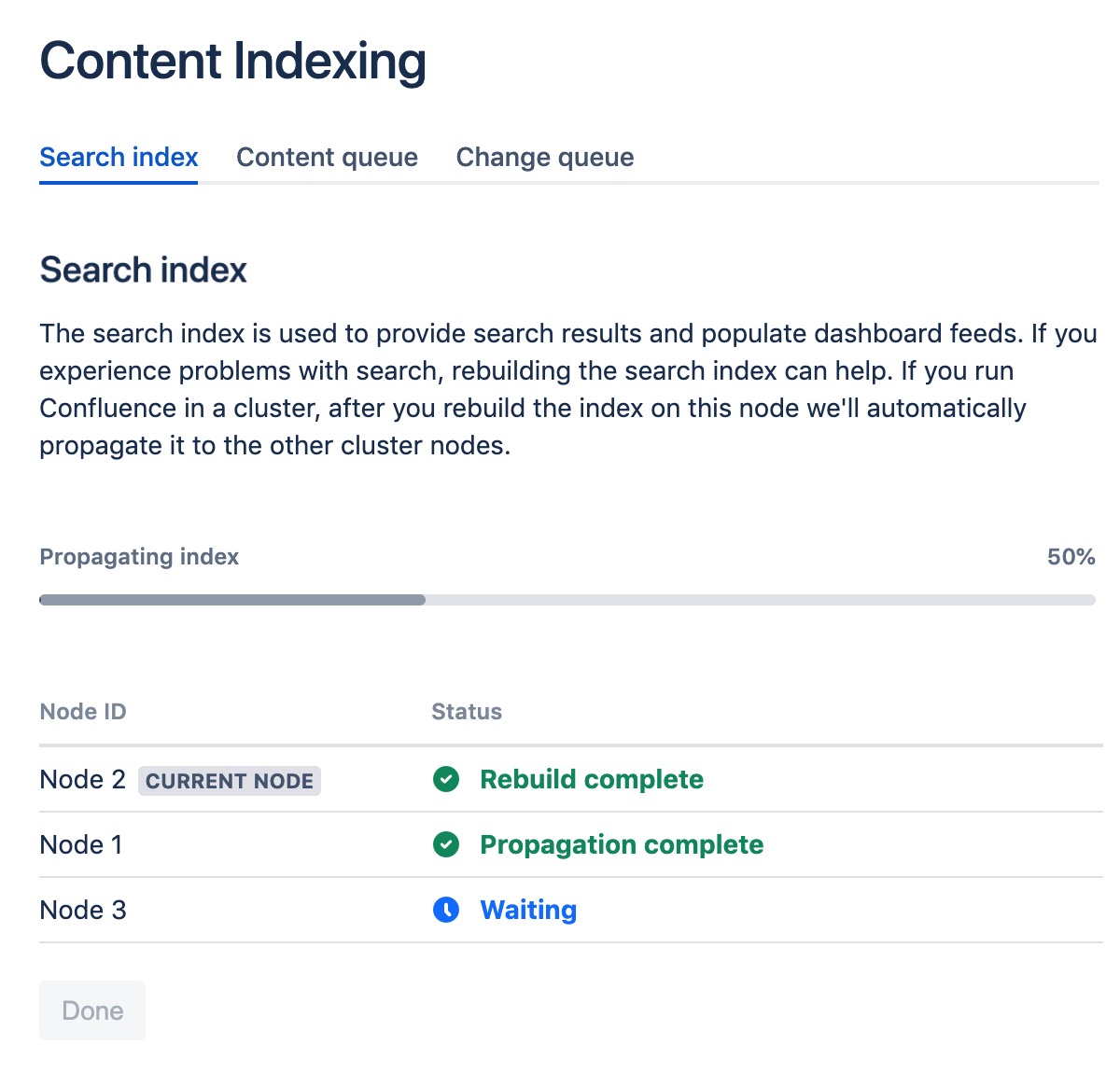
Propagate the search index to your cluster
If you're running Confluence in a cluster, once the index is rebuilt on the current node, we'll automatically propagate the index files to all the other nodes in the cluster.
Screenshot: The Content Indexing screen showing progress as the index is propagated to each node in the cluster.
The index files will only be propagated to nodes that have joined the cluster. If Confluence is not running on a node, we won't be able to propagate the index to that node.
If there's a problem, you'll see an error with information about what went wrong, for example, if a node becomes unavailable, or there's insufficient disk space to copy the index.
Impact on end users
Confluence will continue to use the existing index until the new index has been rebuilt successfully. Your users can continue to search and use Confluence, but may experience some performance degradation. This is because rebuilding the index increases the load on your server significantly.
Rebuilding the index can take several hours. The amount of time depends on the number, type, and size of pages and attachments in your site, the amount of memory allocated, and disk throughput.
If you have a large site, there are some things you can do to reduce the impact on your users:
- If you're running Confluence on a single node, kick off the rebuild on a weekend, or during a scheduled maintenance window.
- If you're running Confluence in a cluster, remove the node rebuilding the index from your load balancer. Once propagation is complete, you can add the node back into the pool.
Disk space requirements
You'll need enough free disk space in your home directory (or local home directories if you're running Confluence in a cluster) to temporarily accommodate two full copies of your index. This is because the existing index is not removed until the new index is ready.
If you're running Confluence in a cluster, you'll also need enough free space in your shared home directory to accommodate an additional index snapshot.
Location of search indexes
You can find the Confluence index in the <home-directory>/index directory.
If you're running Confluence in a cluster, a full copy of the Confluence indexes are stored in the <local-home>/index directory on each Confluence node. A journal service keeps each index in sync.
If you need to see the contents of the search index for any reason, there is a tool you can use to browse the index directly. See How to view the contents of the search index in Confluence Server and Data Center.
Index recovery in a cluster
If you run Confluence in a cluster, a snapshot of the search index is also stored in the shared home directory. These snapshots are created by the Clean Journal Entries scheduled job which, by default, runs once per day.
When you start a Confluence node it will check whether its index is current, and if not, it will request a recovery snapshot from the shared home directory. If a snapshot is not available, it will generate a snapshot from a running node (with a matching build number). Once the recovery snapshot is extracted into the index directory, Confluence will continue the startup process. The journal service will then make any further updates required to bring the index up to date.
If the snapshot can't be generated, or is not received in time, existing index files will be removed and Confluence will perform a reindex on that node. If your index is very large or your file system slow, you may need to increase the time Confluence waits for the snapshot to be generated using the confluence.cluster.index.recovery.generation.timeout system property.
Index recovery only happens on node startup, so if you suspect a problem with a particular cluster node's index, restart that node to trigger index recovery.
The index recovery snapshot isn't used when you manually rebuild your index from the UI. The rebuild process generates a brand new snapshot, before propagating it to other nodes in the cluster.
Troubleshooting
If you have problems rebuilding the search index, the following may help.
Can't rebuild the index
If you're unable to rebuild the index from the Confluence UI, or if you still have problems with search after rebuilding the index, you may need to rebuild the index from scratch. The way you do this depends on whether Confluence is running in a cluster:
- How to Rebuild the Content Indexes From Scratch on Unclustered Confluence
- How to Rebuild the Content Indexes From Scratch
Can't access content Indexing page
If the content indexing page does not load properly, and you see a "We can't check the status of your index, you may have lost your connection, refresh the page to try again" error, try updating your browser to the latest version.
Poor performance while rebuilding the index
If you experience stability problems while the index is being rebuilt, you can reduce the number of threads Confluence should use to rebuild the index. Set the reindex.thread.count system property to define the maximum number of threads that can be used.
If both reindex.thread.count and index.queue.thread.count are unset, the reindex thread count defaults to the number of CPUs on that Confluence server.
Out of memory errors while rebuilding the index
If you experience out of memory errors while rebuilding the index, increasing the heap memory available to Confluence may help. See Fix java.lang.OutOfMemoryError in Confluence.
Rebuild index failed to propagate to other nodes in the cluster
This generally happens when there is not enough free disk space for the local home directory on each node to accommodate two copies of the index. See Failed to propagate index in Confluence Data Center 7.7 and later to find out how to re-try the propagation.