Use diff transcoding
Bitbucket Data Center supports transcoding for diffs. This allows it to convert files in encodings like EUC-JP, GB18030 and UTF-16 to UTF-8, so they are processed correctly by git diff, which only supports UTF-8. Similar transcoding has been applied to the Bitbucket source view since it was released, so this change brings the diff view in line with the source view. Diff transcoding is applied to commit and pull request diffs, as well as the diff-to-previous view.
Git for Windows, formerly known as msysgit, has known issues with Unicode paths. Diff transcoding works on all supported versions of Git for Windows, but 1.8.0 or higher is required to support Unicode paths.
Enabling diff transcoding
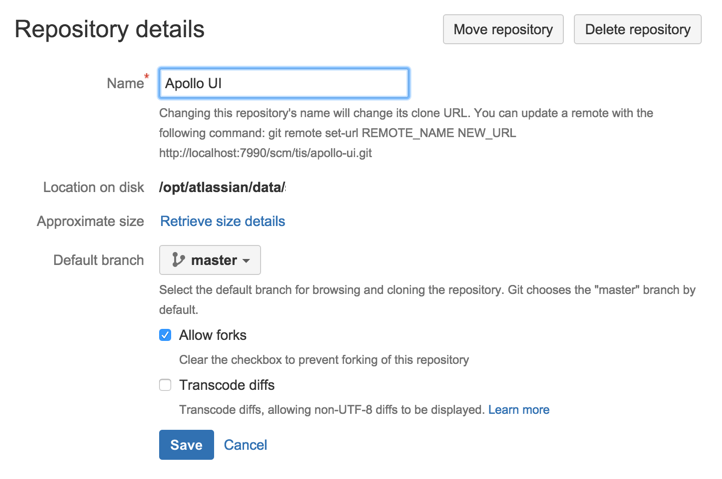
Diff transcoding must be explicitly enabled for each repository (unlike source view transcoding, which is always performed).
Repository administrators can enable diff transcoding on the repository settings page:
Performance and scaling
There's a performance consideration with transcoding. It is implemented using Git's textconv support, so using it adds overhead to displaying diffs. Where possible, the best approach, given git only supports UTF-8 content, is to use UTF-8 encoding so that transcoding is not necessary. In repositories without non-UTF-8 content, diff transcoding should be left disabled. Other encodings are often a necessity, however, and for repositories containing such content enabling diff transcoding allows using the full range of Bitbucket features.