Using branch permissions
Branch permissions allow you to control the actions users can perform on a single branch, branch type, or branch pattern within a repository. Branch permissions provide another level of security within Bitbucket Server, along with user authentication and project, repository and global permissions, that together allow you to control, or enforce, your own workflow or process.
Branch permissions:
- are based on users or groups.
- are actually restrictions, which are checked after project and repository level permissions.
- are used to limit branch access to specific people, or services, that still need write access to the project or repository.
- prevent unauthorized users pushing to or deleting the branch.
- can be based on explicit branch names, branch pattern, branching model.
- currently do not prevent branch creation. Branch permissions will only be enforced on updates to existing branches and tags.
For example, if two developers Xavier and Yves have write access to repository R, but only Xavier has branch permissions on branch B, then Yves won't be able to push to B.
If a user does not have commit access to the branch, an error message will be shown on the Git command line when they try to push a change to the branch. If no branch permissions are defined then anyone with commit access to the repository can push to any branch.
Adding branch permissions
Branch permissions in Bitbucket Server control access to repository branches. You need either project admin, admin or sys-admin permission to set or modify branch permissions.
To add branch permissions:
- Go to a repository in a project.
- Choose Settings > Branch permissions.
- Click Add permission.
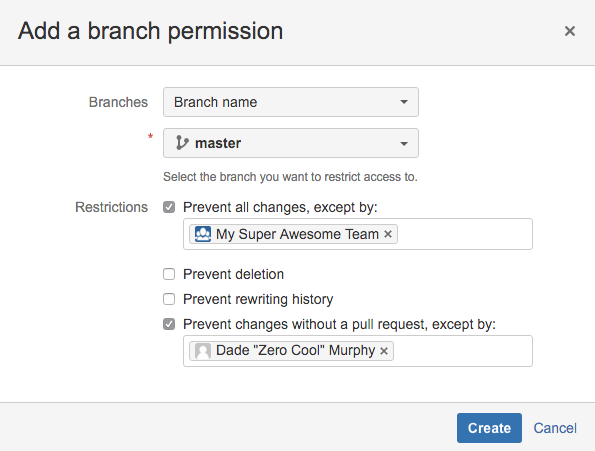
- In the Branches field, select either Branch name, Branch pattern, or Branching model.
- Branch name - select an existing branch by name.
- Branch pattern - specify a branch using branch pattern syntax for matching branch names. See Branch permission patterns for more information about this syntax.
- Branching model - select the branch type to restrict access to. Read more about branching models.
- Select the type of actions you want to prevent.
- Prevent all changes - prevents pushes to the specified branch(es) and restricts creating new branches matching the specified branch(es) or pattern.
- Prevent deletion - prevents branch and tag deletion. See Branch permission patterns for information about specifying tags.
- Prevent rewriting history - prevents history rewrites on the specified branch(es) - for example by a force push or rebase.
- Prevent changes without a pull request - prevents pushing changes directly to the specified branch(es); changes are allowed only with a pull request.
- Optional: Add exemptions for any of the selected restrictions. Adding a user, group, or SSH access key as an exemption means that it will not apply to them. This is not required; not adding any exemptions means the restriction will apply to everyone.
Click Create to finish.
You can always change the permissions for a branch later, if necessary.