Running Jira Data Center in a cluster
Jira Data Center allows you to run a cluster of multiple Jira nodes, providing high availability, scalable capacity, and performance and scale. We’ll tell you about the benefits, and give you an overview of what you’ll need to run Jira in a clustered environment.
Ready to get started? See Set up a Jira Data Center cluster.
Benefits of clustering
Clustering is designed for enterprises with large or mission-critical Data Center deployments that require continuous uptime, instant scalability, and performance under high load.
Here are some of the benefits:
- High availability and failover
If one node in your cluster goes down, the other take on the load, ensuring your users have uninterrupted access to Jira. - Performance and scale
Each node added to your cluster increases concurrent user capacity, and improves response time as user activity grows. - Instant scalability
Add new nodes to your cluster without downtime or additional licensing fees. Indexes and apps are automatically synced.
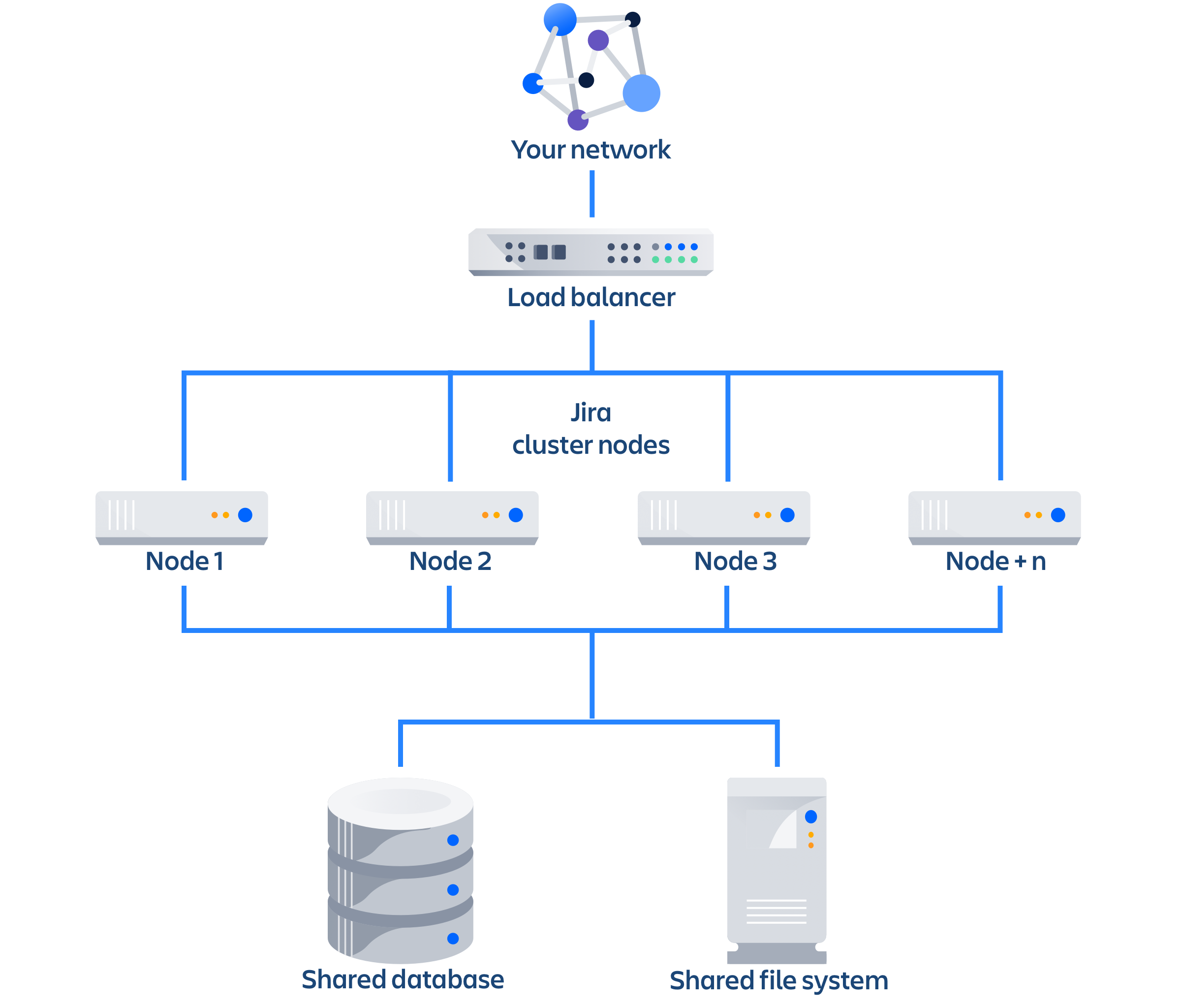
Architecture
The image below shows a typical configuration:
As you can see, a Jira Data Center cluster consists of:
Multiple identical application nodes running Jira Data Center.
A load balancer to distribute traffic to all of your application nodes.
A shared file system that stores attachments, and other shared files.
A database that all nodes read and write to.
All application nodes are active and process requests. A user will access the same Jira node for all requests until their session times out, they log out, or a node is removed from the cluster.
Learn more
Infrastructure and requirements
The choice of hardware and infrastructure is up to you. Below are some areas to think about when planning your hardware and infrastructure requirements.
Running Jira Data Center on Kubernetes
If you plan to run Jira Data Center on Kubernetes, you can use our Helm charts. For more information, see Running Jira Data Center on a Kubernetes cluster.
Deploying Jira Data Center on AWS and Azure
If you plan to run Jira Data Center on AWS or Azure, you can use our templates to deploy the whole infrastructure. You’ll get your Jira Data Center nodes, database and storage all configured and ready to use in minutes. For more info, see the following resources:
Server requirements
You should not run additional applications (other than core operating system services) on the same servers as Jira. Running Jira, Confluence and Bamboo on a dedicated Atlassian software server works well for small installations but is discouraged when running at scale.
Jira Data Center can be run successfully on virtual machines.
Cluster nodes requirements
Each node does not need to be identical, but for consistent performance we recommend they are as close as possible. All cluster nodes must:
- be located in the same data center, or region (for AWS and Azure)
- run the same Jira version
- have the same OS, Java and application server version
- have the same memory configuration (both the JVM and the physical memory) (recommended)
- be configured with the same time zone (and keep the current time synchronized). Using ntpd or a similar service is a good way to ensure this.
You must ensure the clocks on your nodes don't diverge, as it can result in a range of problems with your cluster.
How many nodes?
Your Data Center license does not restrict the number of nodes in your cluster. The right number of nodes depends on the size and shape of your Jira instance, and the size of your nodes. See our Jira Data Center size profiles guide for help sizing your instance. In general, we recommend starting small and growing as you need.
Memory requirements
We recommend that each Jira node has a minimum of 8GB RAM. This would be sufficient for a single Server instance with a small number of projects (up to 100) with 1,000 to 5,000 issues in total and about 100-200 users.
To get an idea on how large and complex your Jira instance is, see Jira Data Center size profiles.
The maximum heap (-Xmx) for the Jira application is set in the setenv.sh or setenv.bat file. The default should be increased for Data Center. We recommend keeping the minimum (Xms) and maximum (Xmx) heap the same value.
You can also check the details of our public Jira Data Center instances. See Jira Data Center sample deployment.
Database
You should ensure your intended database is listed in the current Supported platforms. The load on an average cluster solution is higher than on a standalone installation, so it is crucial to use the a supported database.
You must also use a supported database driver, which should be listed in supported platforms linked above. For more detailed instructions on connecting Jira to a database, see Connecting Jira applications to a database.
Additional requirements for database high availability
Running Jira Data Center in a cluster removes the application server as a single point of failure. You can also do this for the database through the following supported configurations:
Amazon RDS Multi-AZ: this database setup features a primary database that replicates to a standby in a different availability zone. If the primary goes down, the standby takes its place.
Amazon PostgreSQL-Compatible Aurora: this is a cluster featuring a database node replicating to one or more readers (preferably in a different availability zone). If the writer goes down, Aurora will promote one of the writers to take its place.
The AWS Quick Start deployment option allows you to deploy Jira Data Center with either one, from scratch. If you want to set up an Amazon Aurora cluster with an existing Jira Data Center instance, refer to Configuring Jira Data Center to work with Amazon Aurora.
Shared home and storage requirements
All Jira cluster nodes must have access to a shared directory in the same path. NFS and SMB/CIFS shares are supported as the locations of the shared directory. As this directory will contain large amount of data (including attachments and backups) it should be generously sized, and you should have a plan for how to increase the available disk space when required.
Load balancers
We suggest using the load balancer you are most familiar with. The load balancer needs to support ‘session affinity’. If you're deploying on AWS you'll need to use an Application Load Balancer (ALB).
Here are some recommendations when configuring your load balancer:
Queue requests at the load balancer. By making sure the maximum number requests served to a node does not exceed the total number of http threads that Tomcat can accept, you can avoid overwhelming a node with more requests than it can handle. You can check the maxThreads in <install-directory>/conf/server.xml.
Don't replay failed idempotent requests on other nodes, as this can propagate problems across all your nodes very quickly.
Using least connections as the load balancing method, rather than round robin, can better balance the load when a node joins the cluster or rejoins after being removed.
Many load balancers require a URL to constantly check the health of their backends in order to automatically remove them from the pool. It's important to use a stable and fast URL for this, but lightweight enough to not consume unnecessary resources. The following URL returns Jira’s status and can be used for this purpose.
| URL | Expected content | Expected HTTP status |
|---|---|---|
http://<jiraurl>/status | {"state":"RUNNING"} | 200 OK |
Here are some recommendations, when setting up monitoring, that can help a node survive small problems, such as a long GC pause:
- Wait for two consecutive failures before removing a node.
- Allows existing connection to the node to finish, for say 30 seconds, before the node is removed from the pool.
For more info, see Load balancer configuration options and Load balancer examples.
Network adapters
Use separate network adapters for communication between servers. Cluster nodes should have a separate physical network (i.e. separate NICs) for inter-server communication. This is the best way to get the cluster to run fast and reliably. Performance problems are likely to occur if you connect cluster nodes via a network that has lots of other data streaming through it.
App compatibility
The process for installing Marketplace apps (also known as add-ons or plugins) in a Jira cluster is the same as for a standalone installation. You will not need to stop the cluster, or bring down any nodes to install or update an app.
The Atlassian Marketplace indicates apps that are compatible with Jira Data Center. Learn more about Data Center approved apps
Ready to get started?
Head to Set up a Jira Data Center cluster for a step-by-step guide to enabling and configuring your cluster.