Live Monitoring Using the JMX Interface
JMX (Java Management Extensions API) allows you to monitor the status of your Confluence instance in real time. JMX uses objects called MBeans (Managed Beans) to expose data and resources from your application, providing useful data such as the resource usage of your instance and its database latency, allowing you to diagnose problems or performance issues.
On this page, we'll guide you through how to use JConsole to monitor Confluence locally and remotely. JConsole is included in the Java Development Kit (JDK), but you can use any JMX client.
This page also contains information about In-product diagnostics available through JMX.
This guide provides a basic introduction to the JMX interface and is provided as is. Our Support team can help you troubleshoot a specific Confluence problem, but aren't able to help you set up your monitoring system or interpret the results.
Monitor Confluence using JMX
Monitor Confluence remotely using your APM
To monitor Confluence in your Application Performance Monitoring (APM) tool, you'll need to install a JMX exporter to transform theJMX MBeans into the right format for your tool. See Monitor application performance to find out how to do this.
If you don't have an Application Performance Monitoring (APM) system, we've created a guide to get you started with Prometheus and Grafana, including some template dashboards that you can use as a jumping off point. See Monitor Confluence with Prometheus and Grafana.
Monitor Confluence remotely using JConsole
Remote monitoring is recommended for production systems, as it does not consume resources on your Confluence server.
To monitor remotely:
Add the following properties to your
setenv.sh/setenv.batfile. The port can be any port that is not in use.set CATALINA_OPTS=-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote %CATALINA_OPTS% set CATALINA_OPTS=-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=8099 %CATALINA_OPTS%Decide how you will secure your remote connection. See Remote Monitoring and Management for more information.
Although it is possible to disable authentication, we do not recommend doing this on a production system.- Start JConsole (you'll find it in the
bindirectory of the JDK installation directory). - Select Remote Process.
- Enter your hostname and port (this is the port you specified earlier, not the Confluence port).
- Click Connect.
See Using JConsole for more information on remote monitoring.
Monitor Confluence locally using JConsole
If you are troubleshooting a particular issue, or only need to monitor Confluence for a short time, you can use local monitoring. Local monitoring can have a performance impact on your server, so its not recommended for long-term monitoring of your production system.
To monitor locally:
Start JConsole (you'll find it in the
bindirectory of the JDK installation directory)- Select Local Process.
Select the Confluence process. It will be called something like
org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap start
See Using JConsole for more information on local monitoring.
Write JMX metrics to a log file
You can also choose to write the following JMX metrics to a log file. This is useful when you are troubleshooting a problem.
- CacheStatistics
- IndexingStatistics
- MailTaskQueue
- RequestMetrics
- SystemInformation
- ThreadPool
- OS
- GC
- Threading
- TomcatManager
- RequestProcessor
To write JMX metrics to a log file:
- Go to Administration menu , then General Configuration > Scheduled jobs
- Enable the Log JMX Metrics job.
This job runs once per minute by default, and writes metrics to the <local-home/logs/atlassian-confluence-jmx.log file. See Working with Confluence Logs
Disable JMX monitoring
To diable JMX monitoring:
- Go to Administration menu , then General Configuration > Monitoring.
- Deselect JMX monitoring.
This will also disable App monitoring, as it requires JMX to be enabled.
Confluence MBeans
You can use the following Confluence MBeans to see live information about your Confluence instance.
CacheStatistics
This MBean shows information about Confluence caches. This info can also be found on the Cache Statistics page.
IndexingStatistics
This MBean shows information related to search indexing. Here's some useful attributes.
Property name | Function | Values |
|---|---|---|
Flushing | Indicate whether the cache is currently flushing | True/False |
LastElapsedMilliseconds | Time taken during last indexing | Milliseconds |
TaskQueueLength | Shows number of tasks in the queue | Integer |
| ReIndexing | Indicates whether Confluence is currently reindexing | True/False |
SystemInformation
This MBean shows information such as the Confluence version and uptime. This info can also be found on the System Information page.
Property name | Function | Values |
|---|---|---|
DatabaseExampleLatency | Shows the latency of an example query performed against the database | Milliseconds |
RequestMetrics
This MBean shows information related to system load and error pages served.
Property name | Function | Values |
|---|---|---|
AverageExecutionTimeForLastTenRequests | Average execution time for the last ten requests. | Milliseconds |
CurrentNumberOfRequestsBeingServed | Number of requests being served at this instant. | Integer |
ErrorCount | Number of times the Confluence error page was served. | Integer |
NumberOfRequestsInLastTenSeconds | The number of requests in the last ten seconds. | Integer |
MailServer-SMTPServer
This MBean shows information related to email dispatch attempts and failures. There will be an MBean for every SMTP Mailserver that has been configured in the Confluence instance.
Property name | Function | Values |
|---|---|---|
EmailsAttempted | The number of email messages Confluence has tried to send. | Integer |
EmailsSent | The number of email messages sent successfully. | Integer |
MailTaskQueue
This MBean shows information related to the email workload.
Property name | Function | Values |
|---|---|---|
ErrorQueueSize | Number of errors in the queue. | Integer |
Flushing | Shows state (i.e. flushing, or not) | True/False |
FlushStarted | Time that operation began. | Time |
RetryCount | The number of retries that were performed. | Integer |
TaskSize | Number of email messages queued for dispatch. | Integer |
SchedulingStatistics
This MBean shows information related to current jobs, scheduled tasks and the time that they were last run.
| Property name | Function | Values |
|---|---|---|
| AllJobNames | Shows information on current scheduled jobs including the time they were last run | String |
| CurrentlyRunningJobNames | Lists the scheduled jobs that are currently running | List |
App-specific metrics
Enable app monitoring to expose additional metrics that are useful when troubleshooting issues with Marketplace and custom-built apps.
See App metrics reference for a full list of app-specific metrics.
Additional MBeans
To also monitor Hibernate and Hazelcast (Confluence Data Center only) you will need to add the following properties to your setenv.sh / setenv.bat file first.
set CATALINA_OPTS=-Dconfluence.hazelcast.jmx.enable=true %CATALINA_OPTS%
set CATALINA_OPTS=-Dconfluence.hibernate.jmx.enable=true %CATALINA_OPTS%This will make the Hibernate and Hazelcast MBeans available in your JMX client.
Monitoring high CPU consuming threads
The Top Threads Plugin for JConsole is useful for monitoring whether the CPU is spiking. Use the following command to start JConsole with this plugin:
JConsole -pluginpath /pathto/topthreads.jarIn-product diagnostics available through JMX
We've introduced a set of database connectivity, HTTP connection, and indexing metrics for in-product diagnostics available through JMX.
In-product diagnostics (IPD) provides greater insights for you and our Support into how running instances are operating.
IPD uses additional metrics handling Confluence’s interactions with its database. For example, by using database connectivity metrics, you’ll efficiently identify what in your environment or infrastructure might cause the performance issues.
The feature is enabled by default. Live metrics are available in the following formats:
as new JMX MBeans
as a history of snapshots of the JMX values in the new IPD log file
atlassian-confluence-ipd-monitoring.log.
The log file is also included in the Support Zip file created in the Atlassian Troubleshooting and Support app. If needed, send the zip file to Atlassian Support who has the internal tools to interpret it.
The log file is available in the {confluence_home}\logs folder where you can find all the existing log files. The log file is also included in the Support Zip file created in the ATST plugin. If needed, you can generate the Support Zip file in the Atlassian troubleshooting & support tools plugin and send the file to Atlassian Support, where we have internal tools to interpret it. Learn more about the plugin
Communication
The feature communicates in the following ways:
JMX: JMX MBeans are updated periodically based on an internal schedule.
The log file
atlassian-confluence-ipd-monitoring.log: JMX values are snapshotted and recorded to the log file on a configurable schedule. By default, the JMX values are polled and written to the log file every 60 seconds.
In-product diagnostics metrics
Expand the following sections to learn more about the metrics available for in-product diagnostics.
To use the metrics, make sure you’ve first enabled JMX.
To get more details on cross-product metrics, check the article Interpreting cross-product metrics for in-product diagnostics.
Enabling in-product diagnostics monitoring
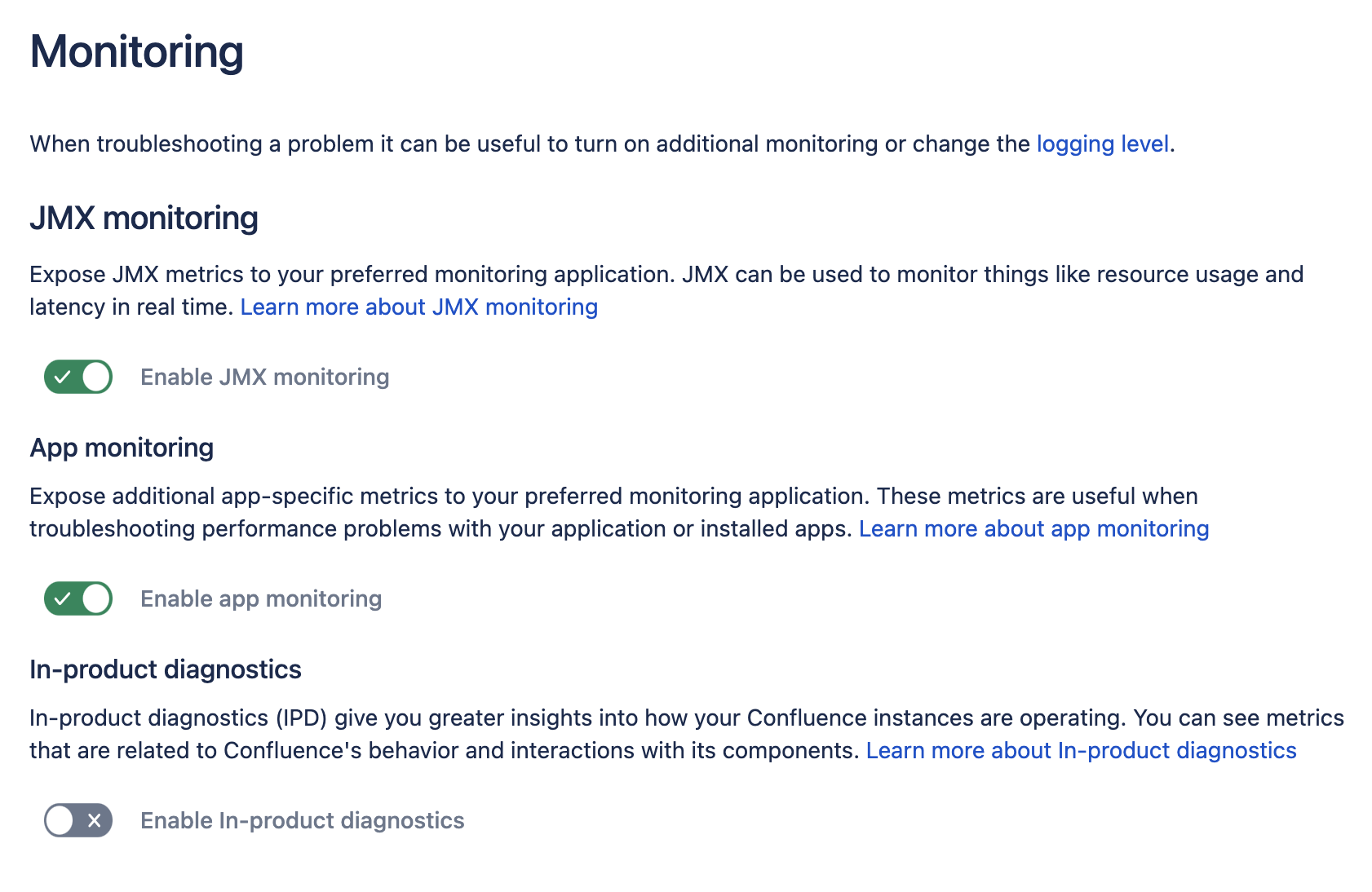
IPD monitoring is enabled by default. To manage it:
Go to Administration menu , then General Configuration
In the left panel, select Monitoring.
Use the Enable in-product diagnostics toggle to enable or disable IPD monitoring.
Screenshot: JMX monitoring settings with in-product diagnostics disabled
Log formatting
Writing to atlassian-confluence-ipd-monitoring.log is done via log4j. Its configuration is managed in log4j.properties.
#####################################################
# In-product diagnostics monitoring logging
#####################################################
log4j.appender.ipdLogAppender=com.atlassian.confluence.logging.ConfluenceHomeLogAppender
log4j.appender.ipdLogAppender.LogFileName=atlassian-confluence-ipd-monitoring.log
log4j.appender.ipdLogAppender.MaxFileSize=20480KB
log4j.appender.ipdLogAppender.MaxBackupIndex=5
log4j.appender.ipdLogAppender.layout=com.atlassian.logging.log4j.NewLineIndentingFilteringPatternLayout
log4j.appender.ipdLogAppender.layout.ConversionPattern=%d %m%n
log4j.logger.ipd-monitoring = INFO, consolelog
log4j.additivity.ipd-monitoring = false
log4j.logger.ipd-monitoring-data-logger = INFO, ipdLogAppender
log4j.additivity.ipd-monitoring-data-logger = falseLog contents
By default, a concise set of data is included in each log entry. An extended set of data can be logged by enabling the confluence.in.product.diagnostics.extended.logging feature flag.
To enable the extended data:
Go to
<CONFLUENCE_URL>/admin/darkfeatures.action, where<CONFLUENCE_URL>is the base URL of your Confluence instance.In the Enable dark feature field, enter
confluence.in.product.diagnostics.extended.loggingSelect Submit. Learn how to manage dark features
To disable the extended data, in the Site Dark Features section, find c
onfluence.in.product.diagnostics.extended.loggingand select remove.
In the following tables, see the structures of the concise and extended logging formats.
The metrics in JMX always go in the extended format.
Concise data
MBean Type | Properties | Attributes |
|---|---|---|
Counter | timestamp label attributes | _count |
Value | _value | |
Statistics | _99thPercentile _max _min _mean |
Extended data
MBean Type | Properties | Attributes |
|---|---|---|
Counter | timestamp label attributes objectName | _count _fifteenMinuteRate _fiveMinuteRate _meanRate _oneMinuteRate _rateUnit |
Value | _value _number | |
Statistics | _50thPercentile _75thPercentile _95thPercentile _98thPercentile _99thPercentile _999thPercentile _count _min _max _mean _stdDev _durationUnit _fifteenMinuteRate _fiveMinuteRate _meanRate _oneMinuteRate _rateUnit |
Definitions of metric attributes
Expand the following sections to learn more about metric attributes.