Mirrors
A Data Center license is required to use this feature. Get an evaluation license to try it out, or purchase a license now.
Also:
Check out the latest on-demand webinar, How to support your geo-distributed teams with Atlassian Data Center.
In this webinar, learn how Atlassian Data Center provides performance at scale for your distributed teams and get access to:
- Best practices on instance setup and configuration for distributed team work
- A deep dive on some of the latest geo-performance features like CDN and mirror farms
- Tips for scaling teamwork globally
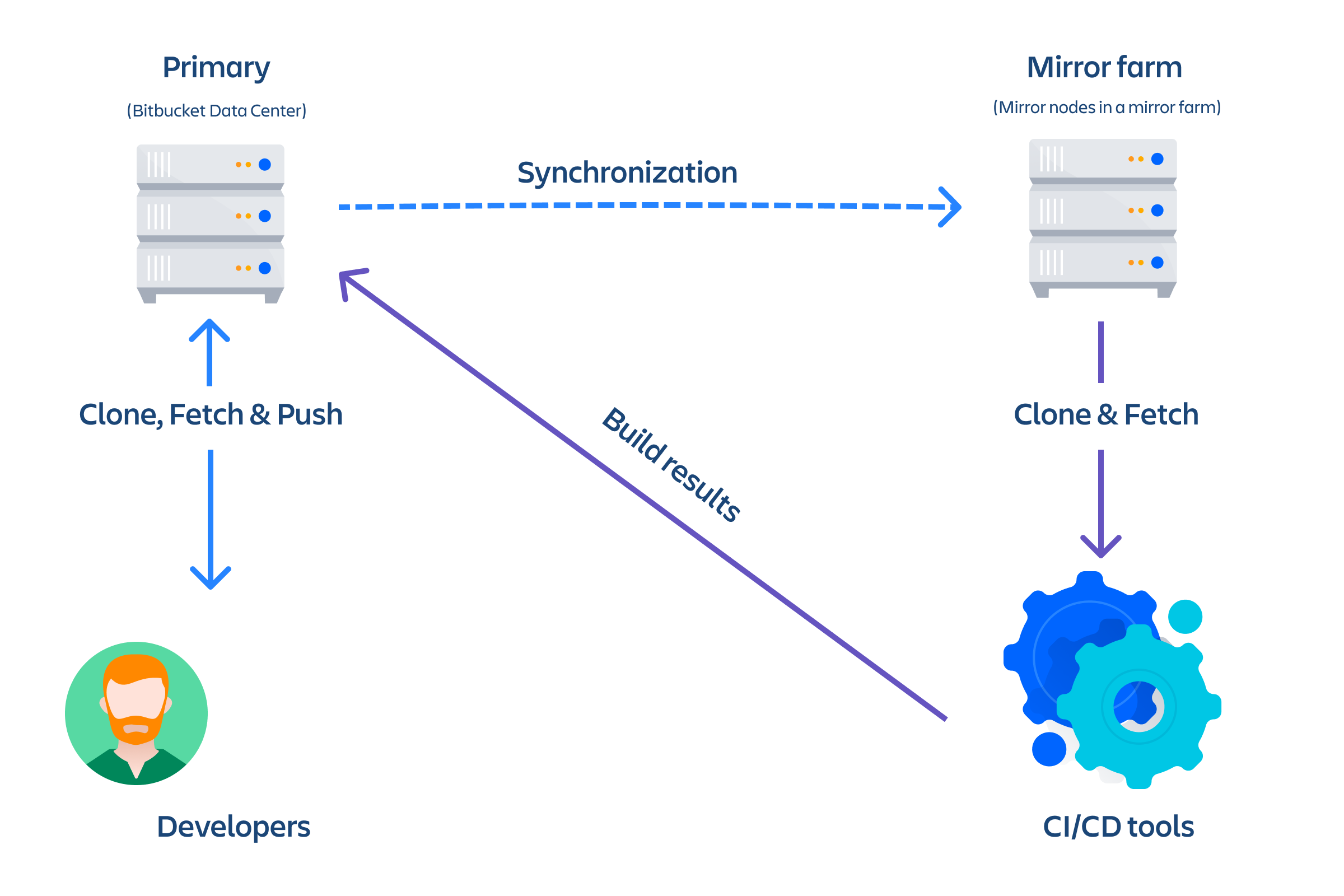
As your team grows, more tests and builds are required to ensure high quality and security of code. Heavy CI/CD load on Bitbucket can degrade the user experience. As a result, we recommend that you redirect CI/CD load to a mirror farm so your primary Bitbucket Data Center can focus on serving real users.
You can provision a mirror or a mirror farm (cluster of mirrors) to serve repositories for CI/CD and release the system resources of your primary Bitbucket Data Center instance.
Mirrors to serve high CI/CD loads
Mirrors can also greatly improve Git clone speeds for distributed teams working with large repositories. Large repositories that take hours to clone from a Bitbucket instance over the Internet from the other side of the world can take minutes when cloned from a local mirror on a fast network.
Many software development teams using Git have large repositories. This is a result of either storing lots of historical information, using monolithic repositories, or storing large binary files (sometimes all three). Companies with distributed software development teams often have little control over the network performance available to them between sites. In combination, this leads to a loss of development time when developers have to wait long periods to clone a large repository from across the world.
Mirroring prevents this lost development time by allowing you to set up live mirrors that host copies of repositories in remote locations. These mirrors automatically keep any repository hosted on them in sync with the primary Bitbucket Data Center instance. Users in those remote locations may clone and fetch repositories from the mirror and get identical content, only faster. You can choose to mirror a selection of projects, or mirror all repositories in all projects from the primary instance.
If you're ready to start mirroring your repositories, you can jump straight to the Set up a mirror or Set up and configure a mirror farm page and follow the steps there, or read on to learn more about the benefits of using a mirror. If you have mirrors already configured, you might be searching for instructions on how to Clone a mirror repository.
How it works
Mirrors run the same application as a full Bitbucket Server instance, but they are configured to mirror a primary Bitbucket Data Center instance, where the primary copy of all your repositories is hosted. When a user clones or fetches from a mirror, the mirror automatically delegates the authentication and authorization of their credentials back to the primary server. No extra user management is required on standalone mirrors or mirror nodes in a farm. All the users, groups, and permissions of the primary Bitbucket instance (whether provided by the built-in user directory and permission system or by your own user directories and/or custom extensions) are always replicated exactly on all mirrors. When a user pushes to a mirror, the mirror chooses two routes based on the push protocol. If the user pushes via the SSH protocol, the request is proxied and a new SSH connection is opened directly from the mirror to the upstream server. If the user pushes via the HTTP(S) protocol, the request is redirected to the upstream server and the user must have access to the upstream.
Self-healing
Self-healing is one of the main design principles for mirroring. Mirrors have the ability to detect and recover from a number of error scenarios, while all operations retry with exponential backoff. Mirroring also includes an anti-entropy system (the farm vet) which verifies the consistency of a mirror against the primary every 3 minutes. For more information and help with monitoring the health of your mirror farm, see Monitoring your mirror farm.
Ready to get started setting up a mirror?
Be sure to read Set up a mirror or Set up and configure a mirror farm for detailed instructions on installing a mirror or mirror farm.
Don't have Bitbucket Data Center yet? Purchase a Data Center license, or get an evaluation license to try it out..