Crowd 2.0 Release Notes
30 July 2009
The Atlassian Crowd team is delighted to present the insanely fast, supremely nested Crowd 2.0.
Highlights of this release:
Responding to your feedback:
More than 220 votes satisfied
Keep logging your votes and issues. They help us decide what needs doing!
Upgrading to Crowd 2.0
You can download Crowd from the Atlassian website. If upgrading from a previous version, please read the Crowd 2.0 Upgrade Notes.
Highlights of Crowd 2.0
Introducing User Aliases
A single user can now have different usernames in different applications. For example, Arthur Dent might have username 'dent@example.com' in your JIRA issue tracker, 'arthur' in your internal Confluence wiki and 'adent' in your public-facing Confluence wiki.
- Using Crowd, Arthur can link a number of usernames as aliases of his main login ID.
- Arthur can log in just once, to any Crowd-connected application. He will be automatically logged into the other applications via single sign-on (SSO).
- Crowd's Administration Console makes it easy for a system administrator to track and manage the username, aliases and application authorizations for each user.
- Crowd's user aliasing allows you to work around the problem that occurs when you want to implement a single user base for a number of existing systems, where users may have different usernames in each system.
- When someone gets married or changes their name, you may wish to rename a user in your LDAP directory, such as Microsoft Active Directory. To avoid problems in applications which do not allow user renaming, you can now link the new LDAP username to an alias in Crowd.
- Some systems may use email addresses as usernames, while in others this may expose users to email spambots. Using Crowd aliasing, you can use different username formats to suit your application requirements.
- Our documentation has the details.
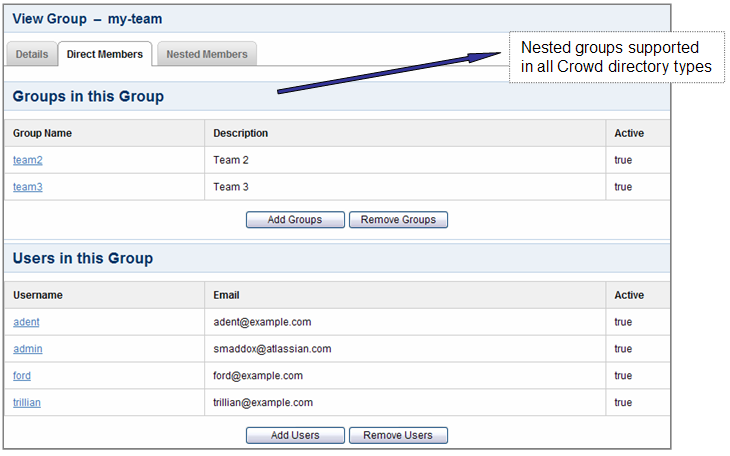
Nested Groups in All Crowd Directories
With Crowd 1.4, we introduced support for nested groups in Crowd-connected LDAP directories. This means that you can have a group as a member of another group. Now Crowd 2.0 supports nested groups for Crowd Internal and Delegated Authentication directories too. Your custom directories will also support nested groups, provided that they meet the interface requirements of the RemoteDirectory API.
- When verifying a user's login to a Crowd-connected application, Crowd will search the groups mapped to the application plus all their sub-groups.
- When an application requests a list of users in a group, Crowd will present a flat list of users gathered from the requested group and its sub-groups.
Automatic Group Membership for New Users
You can now configure Crowd to assign new users to specific groups automatically.
- You can define default groups for each directory.
- A new user automatically becomes a member of these groups, whether added via the Crowd Administration Console or via a Crowd-connected application.
- Note that the automatic group membership does not work when importing users and groups via Crowd's external user importer.
- You can read more in our documentation.
Improved User and Group Management UI
Looking to relieve the administrative pain that user and group management often entail, we have enhanced the management screens in the Crowd Administration Console and added bulk user and group administration for the first time in Crowd.
- You can add multiple users to a group at the same time.
On the user management side:
- You can add a user to multiple groups at the same time.
- When searching for a user, just enter all or part of a name, username or email address in a single search box to find the matching users.
- The user browser now shows every user's full name, as well as their usernames and email addresses.
Improved Performance
The Crowd team have done a lot of under-the-cover work in this release, chiefly on updating Crowd's database schema. This work will put us in good stead to provide shiny new features in later releases. For Crowd 2.0, the biggest gain is in the performance of Crowd Internal and Delegated Authentication directories. Comparisons of Crowd 2.0 with the previous release have generated the following statistics in our test environment, running on a Crowd Internal directory with 60 000 users, 5 000 groups and 240 000 group memberships.
- Most operations are about twice as fast.
- Retrieving all users is a gigantic 15 times faster. This request is used when an application asks for all users at once, such as when JIRA's cache expires.
- Searching on fields such as name and email address is more than twice as fast.
- Authenticating a user is 60% faster.
We haven't even tried to represent the searchPrincipals and findAllGroupRelationships requests graphically, because the performance improvement is off the charts:
MySQL is 15 times faster.
PostgreSQL is 100 to 1000 times faster.
Improved Database Support
The updated Crowd database schema provides some wins in the area of database support too.
- UTF-8 character encoding is now supported for MySQL databases. Before this release, Crowd required Latin 1 character encoding.
- The Crowd database schema uses case-insensitive table names, so for people who are using PostgreSQL, there is no longer any need for silly quotes in your SQL queries.
- Crowd's mail template size is no longer limited to 255 characters.
New REST API
Crowd 2.0 exposes a new REST API that provides access to resources (data entities) via URI paths. This is useful for developers wanting to integrate Crowd into their application and for administrators needing to script interactions with the Crowd server.
- To use a REST API, your application will make an HTTP request and parse the response.
- You can request a response format of XML or JSON.
- Your methods will be the standard HTTP methods like GET, PUT, POST and DELETE.
- Because the REST API is based on open standards, you can use any web development language to access the API.
Plugin Framework 2.2 and REST Module
Crowd 2.0 supports version 2.2 of the Atlassian Plugin Framework, the latest plugin framework release to date. Crowd now also bundles the new Rest plugin module type. We have used the REST plugin module type to develop the Crowd 2.0 REST APIs mentioned above.
- Developers can use the REST module type to create plugin points easily in Crowd by exposing services and data entities as REST APIs.
- The REST module type also makes it easier to develop cross-application plugins i.e. plugins which work in more than one application, because the module type helps developers to ensure consistency of REST APIs across Atlassian applications.
Other Things Worth Mentioning
- You can now use wildcard IP ranges (CIDR notation) when specifying IP restrictions for an application.
- We now offer full support for Tomcat 6.
- We have enhanced the remote directory API to support finer-grained control in searches. The new API is type safe, supports 'AND' and 'OR' queries and allows you to make finer-grained requests based on primary or custom attributes. For example, you might search for users whose favorite color is 'pink'. The details are in the JavaDocs.